Hello! Today I will tell you what a railway station is, what they are needed for, what they are made of, and also how they are classified. In fact, nothing complicated, you just need to figure it out and translate complex railway concepts into Russian. This is exactly what we will do now. First, let me give you the official definition:
A railway station is the main object of railway transport, one of the types of separate points, which has a track development that allows operations for receiving, sending, crossing and overtaking trains, operations for receiving, issuing cargo, luggage and cargo luggage, servicing passengers, and with developed track devices - shunting work on the formation and disbandment of trains and technical operations with trains.
Wow, how interesting! I got confused while I was writing, so much has been written. But this is the specifics of the railway language, alas, nothing can be done. So, let's continue.
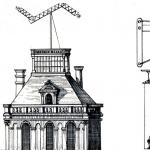
To put it simply in simple language, a railway station is a place where there are many tracks. All. That's it in short. And everything that was given above is the purpose. And if you still don’t understand, look at the photo.
Now it’s definitely clear. Here you can see the development of the route and there are even some buildings in the distance.
PURPOSE
Let's now look at the purpose. The stations are intended for:
- arrival and departure of trains
- crossing and overtaking trains
- performing operations for receiving and issuing cargo and luggage
- passenger services
- formation and disbandment of trains
Of course, there are other functions for which stations are intended; we will focus on the main ones. What is the reception and departure of trains should be clear to everyone. I'm right? I think yes. I’ll briefly explain the rest. A crossing is when trains traveling towards each other somehow miraculously do not collide. In fact, one of the trains moves to another track using a switch and waits for the oncoming train to pass by on the adjacent track, and then again uses the switch to enter the main track and moves on. This is only possible at stations.

Overtaking is practically the same as crossing, only the trains travel one after another. And if one of the trains needs to be ahead, then the train in front moves to another track at the station and stops, and the second train overtakes it along the main track. Typically, passenger trains are released ahead in this way, since their speed is higher than that of freight trains. Overtaking points can also be used for overtaking.
OPERATIONS WITH CARGO
To carry out operations for receiving and issuing cargo and luggage, in other words, for loading and unloading cargo and luggage, as well as serving passengers, stations are equipped with special devices - platforms, warehouses, loading and unloading areas, sorting platforms and slides. If it is necessary to unload and load large volumes of cargo (for example: coal, ore), entire railway parks are equipped at stations, located separately from the main station fleet, connected to it by additional tracks.
Railroad transport is designed to transport large volumes of cargo and, naturally, for this purpose they try to make trains as long as possible. It is not always possible to include only one type of cargo from one sender. Taking into account these restrictions, trains are formed and disbanded at stations, that is, completely different cargoes can be included in one train - liquid cargo (gasoline, oil, fuel oil), bulk cargo (coal, ore, grain), frozen products in refrigerated cars, containers and others. For this purpose, special rolling stock is constantly operating at the stations - a shunting locomotive, which carries out shunting work (rearranging cars, coupling and uncoupling to trains).

Have you ever wondered how a railway station functions, why locomotives, trains, various special machines are constantly moving and who controls it all? What is your answer? I asked myself questions like these, which is why I work for the railroad now. Naturally, in addition to tracks, stations have various special devices that allow you to control switches and traffic lights. At large stations there is a depot where carriages and locomotives are serviced. You can also tell a lot of interesting things about FC, ShCh, EC, NCH, but now it’s not about that, but about the fact that depending on the size, volume of work and directions, railway stations are classified.
TYPES OF RAILWAY STATIONS
1.According to their purpose and nature of operation, stations are divided into:
- passenger - the main purpose is to work with passengers (passenger service, ticket sales, formation and organization of passenger trains);
- freight stations - carrying out operations with cargo (loading, unloading, processing transportation documents, forming and organizing the movement of freight trains);
- technical stations - performing technical operations with trains (formation of freight trains, prefabricated, export trains, disbanding of trains);
- intermediate stations are small stations intended for crossings, overtaking and other small work with trains. The photo below shows the intermediate station.

Technical stations are in turn divided into:
- Sorting - roughly speaking, at this station, cars are sorted by type of cargo, by senders, by recipients, by directions;
- District stations - these stations are located at a distance of up to 300 kilometers from each other; they house turnover points for locomotives and locomotive crews. In general, for each such point there is a service section - locomotive crews (driver and assistant) pass this section, rest at the turnaround point and go back. that's why it has such a name;
- Pre-port stations - perform operations at the junction of seaports and railways, that is, they reload cargo from ships to wagons and vice versa.
2. There is another classification related to the joining of railways:
- docking station - at such stations, sections with different types of current (direct, alternating) in the contact network are joined;
- junction stations - a station adjacent to at least three directions of the railway (for example: one from the south, the second from the north, the third from the west).
- interstate transmission station - a station located on the border of different states.
- junction interroad station - a railway station located on the border railways(the railway in Russia is divided into roads - so-called regional control centers depending on the region. I work, for example, on the Far Eastern Railway.).
CLASSES OF RAILWAY STATIONS
Depending on how busy the railway station is, what volume, complexity of operations and level of technical equipment the station is divided into 6 classes: extracurricular stations, stations of the first (I), second (II), third (III), fourth (IV) and fifth classes (V).
- Non-class stations - large passenger, freight, and most marshalling stations;
- First class stations - freight, passenger, district;
- Second class - mostly district police officers;
- Stations of the third, fourth, fifth classes are intermediate stations.
This is where I will end my article. In the future, I plan to talk in more detail about the specifics of each station, about the professions of the people working at the stations, and other nuances. Subscribe to updates, share on in social networks, express your opinion - it is especially valuable to me. Thank you for your attention. Bye!
Best regards, Sergey Tkachenko.
In Russia, the railway covers almost all regions of the country. A huge number of different cargoes are sent by rail, many who for the first time decided to send some kind of cargo by rail are faced with a number of questions, and the first question is what railway stations are located close to the place of delivery of the cargo. Each railway station in Russia has its own station code, but not every railway station can accept loaded wagons. The work of a railway station may not be to receive loaded cars, but to sort the cars. The organization of the work of a railway station consists of the processing of wagons; the freight railway station organizes the placement of wagons for loading and unloading of wagons.
Our website contains complete information about all railway stations in Russia. All railway stations and junctions are divided into roads, which are responsible for railway stations in certain districts of Russia. All railway stations in Russia are assigned to specific railways and all have railway station codes. The distance between railway stations may vary, but almost every city in Russia has the nearest railway station.
On our website you can find by the name of the railway stations the railway station you need and find out the station code, or, conversely, by the code of the railway station you can find the name of the railway station.
Our directory contains information about all railway stations at all departments of the railway, the code of the railway station, the name of the railway station, the name of the railway to which the railway station is assigned and the railway station code is assigned.
The directory of railway stations contains a list of railway departments and all railway stations related to them.
By selecting the railway department you need from the list, you can easily find the railway station.
Key words: railway station, operation of a railway station, railway stations and nodes, organization of the work of railway stations, distance between railway stations, railway stations in Russia, codes of railway stations, freight railway station, nearest railway station, passenger railway station, railway freight station, railway marshalling station, new railway station, names of railway stations, directory of railway stations, download railway stations and nodes, list of railway stations, old railway station, border of a railway station, railway station, name of a railway station, railway station codes, railway station code, code Russian Railways stations, codes of railway stations, codes of railway stations in Russia, codes of destination stations, codes of railway stations in Russia, find out the station code, codes of railway stations in Russia, decoding the station code, find out the code of the station, railway stations, names of railway stations, railway stations Russian stations, Oktyabrskaya railway station, distance between railway stations, northern railway stations, Gorkovskoe railway station, St. Petersburg railway stations, list of railway stations.
Railway network Russian Federation quite extensive. It consists of several sections of highways, which are owned by Russian Railways OJSC. Moreover, all regional roads are formally branches of JSC Russian Railways, while the company itself acts as a monopolist in Russia:

The road runs through the territory of the Irkutsk and Chita regions and the republics of Buryatia and Sakha-Yakutia. The length of the highway is 3848 km.
The road runs along two parallel latitudinal directions: Moscow - Nizhny Novgorod - Kirov and Moscow - Kazan - Yekaterinburg, which are connected by roads. The road connects the Central, North-Western and Northern regions of Russia with the Volga region, the Urals and Siberia. The Gorky road borders on the following railways: Moscow (Petushki and Cherusti stations), Sverdlovsk (Cheptsa, Druzhinino stations), Northern (Novki, Susolovka, Svecha stations), Kuibyshevskaya (Krasny Uzel, Tsilna stations). The total developed length of the road is 12066 km. The length of the main railway tracks is 7987 km.


The railway passes through the territory of five constituent entities of the Russian Federation - Primorsky and Khabarovsk territories, Amur and Jewish Autonomous Regions, and the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). Its service area also includes the Magadan, Sakhalin, Kamchatka regions and Chukotka - over 40% of the territory of Russia. Operating length - 5986 km.
The Trans-Baikal Railway runs in the south-east of Russia, through the territory of the Trans-Baikal Territory and the Amur Region, is located next to the border of the People's Republic of China and has the only direct land border railway crossing in Russia through the Zabaikalsk station. Operating length - 3370 km.



The West Siberian Railway passes through the territory of Omsk, Novosibirsk, Kemerovo, Tomsk regions, Altai Territory and partly the Republic of Kazakhstan. The developed length of the main tracks of the highway is 8986 km, the operational length is 5602 km.
The road operates in special geopolitical conditions. The shortest route from the center of Russia to the countries lies through Kaliningrad Western Europe. The road does not have common borders with Russian Railways. The total length of the highway is 1,100 km, the length of the main routes is over 900 kilometers.
The highway passes through four large regions - Kemerovo region, Khakassia, Irkutsk region and Krasnoyarsk region, connecting the Trans-Siberian and South Siberian railways. Figuratively speaking, this is a bridge between the European part of Russia, its Far East and Asia. The operational length of the Krasnoyarsk road is 3160 km. Total length- 4544 kilometers.


The railway stretches from the Moscow region to the Ural foothills, connecting the center and west of the Russian Federation with large socio-economic regions of the Urals, Siberia, Kazakhstan and Central Asia. The road consists of two almost parallel lines running from West to East: Kustarevka - Inza - Ulyanovsk and Ryazhsk - Samara, which connect at the Chishmy station, forming a double-track line ending at the spurs of the Ural Mountains. Two other lines of the road Ruzaevka - Penza - Rtishchevo and Ulyanovsk - Syzran - Saratov run from North to South.
Within its current boundaries, the Moscow Railway was organized in 1959 as a result of the full and partial unification of six roads: Moscow-Ryazan, Moscow-Kursk-Donbass, Moscow-Okruzhnaya, Moscow-Kiev, Kalinin and Northern. The deployed length is 13,000 km, the operational length is 8,800 km.
The Oktyabrskaya Mainline passes through the territory of eleven constituent entities of the Russian Federation - Leningrad, Pskov, Novgorod, Vologda, Murmansk, Tver, Moscow, Yaroslavl regions, the cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg and the Republic of Karelia. Operating length - 10143 km.


The Volga (Ryazan-Ural) railway is located in the southeast of the European part of Russia in the region of the Lower Volga and the middle reaches of the Don and covers the territories of the Saratov, Volgograd and Astrakhan regions, as well as several stations located within the Rostov, Samara regions and Kazakhstan. The length of the road is 4191 km.
The highway connects the European and Asian parts of Russia, stretches from west to east for one and a half thousand kilometers and crosses the Arctic Circle in a northern direction. Passes through Nizhny Tagil, Perm, Yekaterinburg, Surgut, Tyumen. Also serves Khanty-Mansi and Yamalo-Nenets autonomous okrugs. Operating length - 7154 km. The deployed length is 13,853 km.

The highway originates in the center of Russia and extends far to the north of the country. Most of the Northern Mainline is operated in the harsh conditions of the Far North and the Arctic. The unfolded length is 8500 kilometers.


In the service area of the road there are 11 constituent entities of the Russian Federation Southern federal district, it directly borders Ukraine, Georgia and Azerbaijan. The operational length of the highway is 6358 km.

The South-Eastern Railway occupies a central position in the railway network and connects the eastern regions and the Urals with the Center, as well as the regions of the North, North-West and Center with Northern Caucasus, Ukraine and the states of Transcaucasia. The South-Eastern Road borders on the Moscow, Kuibyshev, North Caucasus, and Southern Railways of Ukraine. Operating length - 4189 km.
The South Ural Railway is located in two parts of the world - at the junction of Europe and Asia. It includes Chelyabinsk, Kurgan, Orenburg and Kartalinsk branches. Some railway lines highways pass through the territory of Kazakhstan. The South-Eastern Road borders on the Moscow, Kuibyshev, North Caucasus, and Southern Railways of Ukraine. Operating length - 4189 km. The developed length is over 8000 km.
This list contains links to corresponding lists by region of Russia. Region code List Quantity 01 List of railway stations and platforms of Adygea 18 03 List of railway stations and platforms of Bashkortostan 04 List of railway... ... Wikipedia
- ... Wikipedia
- ... Wikipedia
Moscow All Moscow stations have a transfer to the metro (and thus convenient communication with each other), but also some stations and platforms of railway lines also have a transfer to the metro (from being located next to the metro to a pedestrian ... ... Wikipedia
Main article: Public transport in Moscow Moscow railway junction. In Moscow there are 9 operating railways in ... Wikipedia
Main article: Public transport in Moscow Moscow railway junction. There are 9 operating railway stations in Moscow and it is planned to build three more Euro Stations, a station in the area of the station... Wikipedia
City bus Ikarus 280 Public transport of Moscow city and suburban passenger traffic ... Wikipedia
City bus "Ikarus 280" Public transport of Moscow, urban and suburban passenger transport of Moscow, accessible and in demand for use by the general public, with regular routes. According to a narrow interpretation... ... Wikipedia
City bus "Ikarus 280" Public transport of Moscow, urban and suburban passenger transport of Moscow, accessible and in demand for use by the general public, with regular routes. According to a narrow interpretation... ... Wikipedia