Unit segment, coordinates, number beam
This template can be used as a starting file for a presentation educational materials group of listeners.
Sections
To add sections, right-click the slide. Sections allow you to organize your slides and organize collaboration between multiple authors.
Notes
Use the notes section to post speaker notes or additional information for the audience. As your presentation plays, these notes appear in the presentation view.
Pay attention to font size (important for legibility for low vision, video recording and screen reading)
Matching colors
Pay special attention to graphs, diagrams and labels.
Please note that printing will be done in black and white or grayscale. Perform a test print to ensure the color difference is maintained when printing in black and white or grayscale.
Charts, tables and graphs
Keep it simple: use consistent, simple styles and colors whenever possible.
Label all charts and tables.
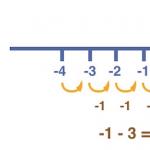
Let's draw a ray with its origin at point A.
From the beginning of the ray we will lay equal segments one after another.

At the beginning of the ray, point A, we put the number zero and renumber the ends of the segments one after the other.
This is a number beam.

The beginning of the number line corresponds to the number 0.
On the number line, any number can be represented by a dot, no matter how large it is
 3, 98. "width="640"
3, 98. "width="640" Using the number beam it is easy to compare:
the more to the right the point is from the beginning of the ray, the larger number she portrays.

Let's secure it!
Using the number line, name all the numbers that are less than 8 and all the numbers that are greater than 8.

Write down which numbers on the number line correspond to the points A, B, C, K.

Coordinate beam
To draw a coordinate ray you need :
- mark a point ABOUT – beginning of the beam at the intersection of cells;
- move the beam so that it goes from left to right
Point O has coordinate 0
To build unit segment :
- mark the fall point on the ray A
- let's give it a point And coordinate 1
Distance from point ABOUT to the point A ,
those. the distance from 0 to 1 is unit segment .
The coordinate ray is not built if not unit segment .

Unit segment
A single segment can have different lengths
For example, we need to build a coordinate ray
With a unit segment equal to two cells
To do this you need:
- build a beam (according to the rules discussed above)
- count from point ABOUT two cells
- mark a point and give it a coordinate 1
- distance from 0 before 1 , equal to two cells
and there is unit segment
Below is a coordinate ray with single segment
equal to five cells

Coordinates
As an example of a coordinate ray we can take
an ordinary ruler.
A unit segment of a ruler is 1 cm
unit segment
Let a coordinate ray be given, unit segment whom
equals 3 cells .
Let's mark a point on it B with coordinate 3 .
To mark a point IN necessary:
- from point ABOUT set aside three pieces, one after the other.
- these segments must be the same length and equal to a unit segment .
- at the end of the third segment mark a point IN And
give her the coordinates 3

Exercise 1
a) Draw coordinate ray With single segment,
equal to 4 cells
Check on this beam points :
A (2), WITH (1) , L (5)
b) Draw coordinate ray With single segment,
equal to 7 cells
Check on this beam points :
A (2), WITH (1), D (5)

Task 2
Dan coordinate ray
Write what it is equal to unit segment
Write coordinates of points :
To write down what the coordinate of a point is:
- write the letter that represents the point
- write the number corresponding to the coordinate in brackets
For example: dot A has a coordinate 1 will be written as A(1)
To conveniently display a fraction on a coordinate ray, it is important to choose the correct length of a unit segment.
The most convenient way to mark fractions on a coordinate ray is to take a single segment of as many cells as the denominator of the fractions. For example, if you want to depict fractions with a denominator of 5 on a coordinate ray, it is better to take a unit segment 5 cells long:
![]()

In this case, depicting fractions on a coordinate beam will not cause difficulties: 1/5 - one cell, 2/5 - two, 3/5 - three, 4/5 - four.
If you need to mark fractions on the coordinate ray with different denominators, it is desirable that the number of cells in a unit segment is divisible by all denominators. For example, to depict fractions with denominators 8, 4 and 2 on a coordinate ray, it is convenient to take a unit segment eight cells long. To mark the desired fraction on the coordinate ray, we divide the unit segment into as many parts as the denominator, and take as many such parts as the numerator. To represent the fraction 1/8, we divide the unit segment into 8 parts and take 7 of them. To portray mixed number 2 3/4, count two whole unit segments from the beginning, and divide the third into 4 parts and take three of them:
![]()

Another example: a coordinate ray with fractions whose denominators are 6, 2 and 3. In this case, it is convenient to take a segment six cells long as a unit:

A single segment is usually marked on each of the axes.
Unit segment in mathematics
The role of unit in mathematics is extremely important. The unit interval, as a set of positive numbers but not exceeding one, is one of the main sets for constructing examples in all areas of mathematics.
A lot of certain mathematical quantities lie on a unit segment. For example: probability, domain of definition and domain of significance of many basic functions.
In view of this, as well as another, the operation of normalizing a set of numbers is often carried out, mapping it in various images onto a unit segment.
Single segment in crystallography
A unit segment is a segment cut off by a unit face on each of the crystallographic axes.
see also
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what a “Single Segment” is in other dictionaries:
Or the unit vector (unit vector of a normalized vector space) is a vector whose norm (length) is equal to one. Unit vector ... Wikipedia
General name for parametric curves whose image contains a square (or, more generally, open regions of space) Contents 1 Properties 2 Examples 3 Generalizations ... Wikipedia
In a broad sense, the area of mathematics that studies topology. properties decomp. math. and physical objects. Intuitively, to topological These include high-quality, stable properties that do not change with deformation. Math. formalization of the idea of topological properties... ... Physical encyclopedia
Methods for obtaining numerical solutions to various problems by means of graphical constructions. G.v. (graphic multiplication, graphic solution equations, graphical integration, etc.) represent a system of constructions that repeat or replace... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
Hausdorff's theorem (or paradox) is a statement proven in set theory about the existence of a countable subset of a two-dimensional sphere, the complement of which can be represented as the union of three disjoint sets, and, ... ... Wikipedia
Hausdorff's theorem (or paradox) is a statement proven in set theory about the existence of a countable subset T of a two-dimensional sphere S2, the complement of which can be represented as the union of three disjoint sets A, B and C,... ... Wikipedia
- (fibred space) one of the foundations. structures studied in topology. In modern physics, ch. arr. in the theory of elementary particles, the concept of R. and associated mathematics. structures (connectivity, etc.) is the most. adequate language for... Physical encyclopedia
Over a topological space (cellular partition) X is a space (cellular partition) where is a unit segment, and the slash denotes the operation of identifying a subspace with a single point. A superstructure over a punctuated space(X, x... Mathematical Encyclopedia
This article lacks links to sources of information. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You can... Wikipedia
Number beam ray on which the dots indicate integers. The distance between the points is equal to the unit of measurement (unit segment), which is specified conditionally. Each point is assigned a number, starting with number 1. The beginning of the ray... ... Wikipedia
A single segment is usually marked on each of the axes.
Unit segment in mathematics
The role of unit in mathematics is extremely important. The unit interval, as a set of positive numbers but not exceeding one, is one of the main sets for constructing examples in all areas of mathematics.
A lot of certain mathematical quantities lie on a unit segment. For example: probability, domain of definition and domain of significance of many basic functions.
In view of this, as well as another, the operation of normalizing a set of numbers is often carried out, mapping it in various images onto a unit segment.
Single segment in crystallography
A unit segment is a segment cut off by a unit face on each of the crystallographic axes.
see also
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
- IZH-61
- Black Kholunitsa (river)
See what a “Single Segment” is in other dictionaries:
Unit vector- or unit vector (unit vector of a normalized vector space) a vector whose norm (length) is equal to one. Unit vector ... Wikipedia
Peano curve - common name for parametric curves whose image contains a square (or, more generally, open regions of space) Contents 1 Properties 2 Examples 3 Generalizations ... Wikipedia
TOPOLOGY- in a broad sense, the field of mathematics that studies topology. properties decomp. math. and physical objects. Intuitively, to topological These include high-quality, stable properties that do not change with deformation. Math. formalization of the idea of topological properties... ... Physical encyclopedia
Graphics Computing- methods for obtaining numerical solutions to various problems by means of graphical constructions. G.v. (graphic multiplication, graphic solution of equations, graphic integration, etc.) represent a system of constructions that repeat or replace... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
Hausdorff's theorem- Hausdorff’s theorem (or paradox) is a statement proven in set theory about the existence of a countable subset of a two-dimensional sphere, the complement of which can be represented as a union of three disjoint sets, and, ... ... Wikipedia
Hausdorff's paradox- Hausdorff’s theorem (or paradox) is a statement proven in set theory about the existence of a countable subset T of a two-dimensional sphere S2, the complement of which can be represented as the union of three disjoint sets A, B and C,... ... Wikipedia
SEPARATION- (fibred space) one of the foundations. structures studied in topology. In modern physics, ch. arr. in the theory of elementary particles, the concept of R. and associated mathematics. structures (connectivity, etc.) is the most. adequate language for... Physical encyclopedia
SUPERSTRUCTURE- over a topological space (cellular partition) X space (cellular partition) where is a unit segment, and the slash denotes the operation of identifying a subspace with one point. A superstructure over a punctuated space(X, x... Mathematical Encyclopedia
Koch curve- This article lacks links to sources of information. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You can... Wikipedia
Number beam- Numerical ray is a ray on which natural numbers are indicated by dots. The distance between the points is equal to the unit of measurement (unit segment), which is specified conditionally. Each point is assigned a number, starting with number 1. The beginning of the ray... ... Wikipedia
Single segment. ? A single segment can have different lengths. For example, we need to construct a coordinate ray with a unit segment equal to two cells. To do this, you need to: construct a ray (according to the rules discussed above), count two cells from point O, mark the point and give it coordinate 1, the distance from 0 to 1, equal to two cells, is a unit segment. O. 0. 1. Below is a coordinate ray with a unit segment equal to five cells. O. 0. 1.
Slide 6 from the presentation "Coordinate beam". The size of the archive with the presentation is 107 KB.Mathematics 5th grade
summary other presentations“Mathematics 5th grade “Ordinary fractions”” - Subtracting fractions. Reducing fractions. Difference of fractions. Circle. Fractions with the same denominators. Shares. Compare fractions. Adding fractions. What is a fraction? Bigger denominator. Rule for dividing fractions. Fraction. Part of a circle. Add the fractions. Number. Find a piece. Lesson. Work. Considered example. Watermelon. Find the difference. Unequal fractions. Common fractions. Dividing fractions. Multiplying fractions.
“Tasks for solving equations” - Equations. Let's turn on the traffic light. Test for Ivan Tsarevich. Warm up. Independent work. How much Masha paid for the purchase. Examination homework. Game "Magic Number". Answer the questions. Mosquito family. Trial. Physical education minute.
"Journey through Mathematics" - What triangular number represents an equilateral triangle. Tourists want to explore the densely populated parts of the mainland. At breakfast we ate 3/8 of the cake, and at lunch – 5/8 of the cake. A sailboat travels 1 mile in 10 minutes. The tasks of the great pilot. Island of "literature". A journey through the sea of knowledge. To build a ship, you need to cut logs. Lukomorye Island. The Dragon. The coast of “golden hands”. Stop "Kudykiny Gory".
““Simplifying Expressions” Grade 5” - Simplify the expressions. Take the common factor out of brackets. Distributive law. What expressions can be simplified? How to convert an expression. Simplifying expressions. Task. Solving equations. Terms that have the same letter part are called similar. Find the meanings of expressions in a convenient way. Underline similar terms. Determine what is missing in these expressions.
““Percent” 5th grade” - A percentage is the hundredth part of a number. Solve the problem. Percentage of numbers. Let's check. Finding a number by its percentage. Find it. Finding percentages from percentages. Increase the number 56 by 20%. Write the percentages as a decimal. We always take the whole as one or 100%. Interest. Designation. How to express percentages as decimals. You need to multiply this fraction by 100. How to write it decimal using percentages.
“Triangles and their types” - Creative work. Type of triangle. Triangles. Primary update. Solve the puzzle. Geometric period. Triangles can be divided into groups based on their angles. Triangle and its elements. Peaks. How many lines can be drawn through two points? Two equal sides. Triangles around us.