Races are the main groups of human individuals. Their representatives, differing from each other in many small aspects, form one whole, containing certain characteristics that are not subject to change and inherited from their ancestors as well as their essence. These specific characteristics are most evident in the human body, where one can both trace the structure and take measurements, as well as in the innate abilities for intellectual and emotional development, as well as in temperament and character.
Many people believe that the only difference between races is the color of their skin. After all, we are taught this in school, and in many television programs that promote this idea of racial equality. However, as we grow older, and by seriously thinking about this issue and considering our life experiences (and calling on historical facts for help), we can understand that if the races were truly equal, then the results of their activities in the world would be equivalent. Also, from contacts with representatives of other races, one can conclude that their train of thought and action often differs from the train of thought and action of white people. There are definitely differences between us and these differences are a consequence of genetics.
There are only two ways for people to be equal. The first way is to be the same physically. The second is to be the same spiritually. Let's consider the first option: can people be physically identical? No. There are tall and small, thin and plump, old and young, white and black, strong and weak, fast and slow, and a lot of other characteristics and intermediate options. One cannot see any equality among the multitude of individuals.
As for the differences between races, there are many of them, for example, head shape, facial features, degree of physical maturity at birth, brain formation and skull volume, visual and hearing acuity, body size and proportions, number of vertebrae, blood type, bone density, duration pregnancy, the number of sweat glands, the degree of alpha wave emission in the brain of newborns, fingerprints, the ability to digest milk, the structure and location of hair, odor, color blindness, genetic diseases (such as sickle cell anemia), galvanic resistance of the skin, pigmentation of the skin and eyes and susceptibility to infectious diseases.
Looking at so many physical differences, it is foolish to say that spiritual differences do not exist, and on the contrary, we dare to suggest that they not only exist, but are also of decisive importance.
The brain is the most important organ in the human body. It takes up only 2% of a person's weight, but absorbs 25% of all the calories we consume. The brain never sleeps; it works day and night, supporting the functions of our body. In addition to thought processes, it controls the heart, breathing and digestion, and also affects the body's resistance to disease.
In his epic book, The History of Man, Professor Carlton S. Kuhn (former president of the American Anthropological Association) wrote that the average black brain weighs 1,249 grams compared to 1,380 grams for the average white brain, and that the average black brain's volume 1316 cc cm, and a white person - 1481 cubic meters. cm. He also found that the size and weight of the brain is greatest in white people, then come the easterners (Mongoloids), after them blacks and in last place the aborigines of Australia. Differences between races in brain size are largely due to the structure of the skull. For example, any anatomist can look at a skull and determine whether a person belongs to the white or black race; this was discovered as a result of crime investigations, when it turned out that it was possible to determine the race of a found body even if it was almost completely decomposed and only the skeleton remained.
The black skull is narrower with a low forehead. It is not only smaller but also thicker than the average white skull. The hardness and thickness of the blacks' skulls has a direct bearing on their success in boxing, as they can withstand more blows to the head than their white opponents.
The part of the brain contained in the cerebral cortex is the most developed and complex part of it. It regulates the most essential types of mental activity, such as mathematical abilities and other forms of abstract thinking. Dr. Kuhn wrote that there is a big difference between the brain of a Negro and a white one. The anterior lobe of a black man's brain is less developed than that of a white man. Thus, their abilities in the areas of thinking, planning, communication and behavior are more limited than those of whites. Professor Kuhn also found that this part of the brain in blacks is thinner and has fewer convolutions on the surface than in white people, and the development of this region of the brain in them stops at an earlier age than in whites, thereby limiting further intellectual development.
Dr. Kuhn is not alone in his conclusions. The following researchers in the years listed, using various experiments, showed a difference between blacks and whites ranging from 2.6% to 7.9% in favor of whites: Todd (1923), Pearl (1934), Simmons (1942) and Connolly (1950) . In 1980, Kang-cheng Ho and his associates, working at the Case Western Institute of Pathology, determined that the brains of white men are 8.2% larger than the brains of black men, while the brains of white women are 8.1% larger than the brains of black women ( A woman's brain is smaller than a man's brain, but larger as a percentage of the rest of the body).
Black children develop faster than white children. Their motor functions develop quickly along with their mental ones, but later there is a delay and by the age of 5 years, white children not only catch up with them but also have an advantage of about 15 IQ units. The larger brains of white children by age 6 are further evidence of this. (No matter who the IQ tests were taken on, they all showed differences between 15% and 23%, with 15% being the most common result).
Studies by Todd (1923), Wint (1932-1934), Pearl (1934), Simmons (1942), Connolly (1950) and Ho (1980-1981) showed important differences between races in both brain size and development, and hundreds psychometric experiments have further confirmed these 15 units of difference in intellectual development between blacks and whites. However, such research has now been discouraged, and such initiatives would have been met with frantic attempts at suppression, had they taken place. Certainly, the study of biological differences between races seems to be one of the top topics that is taboo to talk about in the United States today.
The findings of Professor Andrei Shuya in a monumental 50-year work on IQ tests, called “Testing the Intelligence of Negroes,” indicate that the intelligence assessment of blacks is on average 15-20 points lower than that of whites. These studies were recently confirmed in the best-selling book, The Bell Curve. The amount of “overlap” (exception cases where blacks score the same number of units as whites) is only 11%. For equality, this value must be at least 50%. According to Professor Henry Garrett, author of Children: Black and White, for every gifted black child, there are 7-8 gifted white children. He also found that 80% of gifted black children are of mixed blood. In addition, researchers Baker, Isaac, Jensen, Peterson, Garrett, Pinter, Shuey, Tyler, and Yerkes agree that blacks are inferior in logical and abstract thinking, numerical calculation, and mental memory.
It should be noted that people of mixed descent perform better than pure-blooded blacks, but lower than pure-blooded whites. This explains why blacks with a light skin tone are more intelligent than those with very dark skin. An easy way for you to check whether this is true or not is to look at black people on TV, famous presenters or artists. Most of them have more white blood than black, and are thus more capable of communicating with whites.
The argument has been made that the IQ test is related to the culture of a particular society. However, this is easy to refute by the fact that Asians, who had just arrived in America and were far from the specifics of American culture (which, of course, cannot be said about American blacks) were ahead of blacks in the tests. Also, the American Indians, who, as everyone knows, are a group of society that is not in the best social position, are ahead of the blacks. And finally, poor whites have a slight advantage, but are ahead even by the upper class of blacks who have fully integrated into American culture.
In addition, every IQ test provided by the US Department of Education, all levels of the military, state, county and city education departments has always shown that blacks are, on average, the same 15% weaker than whites. If this test were even associated with white culture, it would be virtually impossible for every test containing a huge number of different questions to end up aiming for a single number with such precision.
Below is a graph from the US Society for Research in Child Development that shows that a large proportion of black children fall in the low IQ range. Since an IQ of 85 to 115 is considered normal, it can be seen that most black children have an IQ lower. You can also see that many more white children than black children have IQs greater than 100.
The difference in mental strength is not the only mental difference between whites and blacks.
According to the analyzes of J. P. Rushton, blacks are more excitable, more prone to violence, less sexually restrained, more impulsive, more likely to commit crimes, less altruistic, less inclined to follow rules, and less cooperative. Crime statistics, the impulsive and violent nature of the crimes that blacks commit, the fact that schools with mixed students require more discipline and police presence than schools with only white students, and the willingness of a certain part of blacks to take part in causing riots have all been confirmed by observations. Mr Rushton.
“Education, sir, is the development of what exists. From time immemorial, blacks owned the African continent - wealth beyond the limits of poetic fantasies, lands crunchy with diamonds under their feet. But they never raised a single diamond from the dust until the white man showed them its brilliant light. Their lands were crowded with powerful and obedient animals, but they did not even think of harnessing a cart or sleigh. Hunters by necessity, they never made an axe, spear or arrowhead to preserve them after the moment of use. They lived like a herd of bulls, content to nibble on grass for an hour. In a land full of stone and wood, they did not bother to saw a board, cut a single brick, or build a house other than sticks and clay. On the endless ocean coast, next to the seas and lakes, for four thousand years they observed the ripples from the wind on their surface, heard the crash of the surf on the beaches, the howling of the storm above their heads, peered into the foggy horizon, calling them to the worlds that lay on the other side , and not once did the dream of sailing capture them!
At one time, when there was more expression of free thought and the media were not entirely under Jewish control, scholarly books and reference books were clear in their interpretation of the above facts. For example, “Popular Scientific Collection” volume 11, edition 1931, p. 515, states the following in the “Section of Primitive Peoples”: “The conclusion is that the Negro does indeed belong to an inferior race. The capabilities of his brain are weaker, and his structure is simpler. In this regard, alcohol and other drugs that can paralyze self-control are its enemies.” Another example is a direct quote from the section “The Negro” in the Encyclopedia Britannica, 11th edition, p. 244:
“The color of the skin, which is also recognized by the velvety of the skin and the special smell, does not exist due to the presence of any special pigment, but due to the large amount of coloring matter in the Malpighian mucous membrane between the inner and outer layers of the skin. Excessive pigmentation is not limited to the skin, pigment spots are often found in internal organs such as the liver, spleen, etc. Other features found are modified excretory organs, a more pronounced venous system and a smaller brain volume compared to the white race.
Of course, according to the above-mentioned characteristics, the Negro should be classified as a lower level of evolutionary development than the white one, and closer in degree of kinship to the higher anthropoids (monkeys). These characteristics are: the length of the arms, the shape of the jaw, a heavy massive skull with large brow ridges, a flat nose, depressed at the base, etc.
Mentally, the Negro is inferior to the white. F. Manetta's notes, collected after many years of studying blacks in America, can be taken as the basis for describing this race: “Negro children were smart, quick-witted and full of liveliness, but as the period of maturity approached, changes gradually came. The intellect seemed to be clouded, animation gave way to a kind of lethargy, energy was replaced by laziness. We must certainly understand that the development of blacks and whites occurs in different ways. While on the one hand, with the growth of the brain, the cranium expands and is formed in accordance with the shape of the brain, on the other hand, premature closure of the cranial sutures occurs and subsequent compression of the brain by the frontal bones.” This explanation makes sense and may be one of the reasons...”
Why was this information deleted? Simply because it did not correspond to the plans of the government and the media. Please remember that before 1960, racial differences between whites and blacks were internationally known and accepted.
Here are the biological facts about races. We understand that they may be “politically incorrect,” but that doesn’t stop the facts from being facts. There is no more “hate speech” in stating the biological facts that the white race is more intelligent than in saying that human beings are more intelligent than animals, or that some animals are more intelligent than other animals. Science has nothing to do with “hate speech”, it deals with reality.
Based on materials:
Special publication of the “Creation Movement”
local chapter of The Creativity Movement
Humanities
FOUND A WAY TO DETERMINE RACE BY FINGERPRINT

American anthropologists said that a fingerprint can be used to determine whether a person had representatives of the Caucasian or Negroid race in his family. The results of the study were published in the official journal of the American Association of Physical Anthropology; a summary is provided on the website of North Carolina State University.
To conduct the experiment, scientists took fingerprints of the right index finger from representatives of the two groups. The first group (122 people) included African Americans; there were equal numbers of men and women. The second group consisted of Caucasians - 61 women and 60 men. The resulting fingerprints were analyzed for both global and local characteristics. Global features in fingerprinting include, for example, the type of papillary pattern, while local features include changes in the structure of papillary lines.
According to the scientists, these structural changes have characteristic differences between African Americans and Caucasians, such as how the lines bifurcate. The authors noted that they did not find signs indicating the gender of the person who left the print.
The researchers clarified that it is not yet possible to guarantee high recognition accuracy. They hope that, with the necessary refinement, their method of determining ancestry will be useful to both other anthropologists and criminologists.
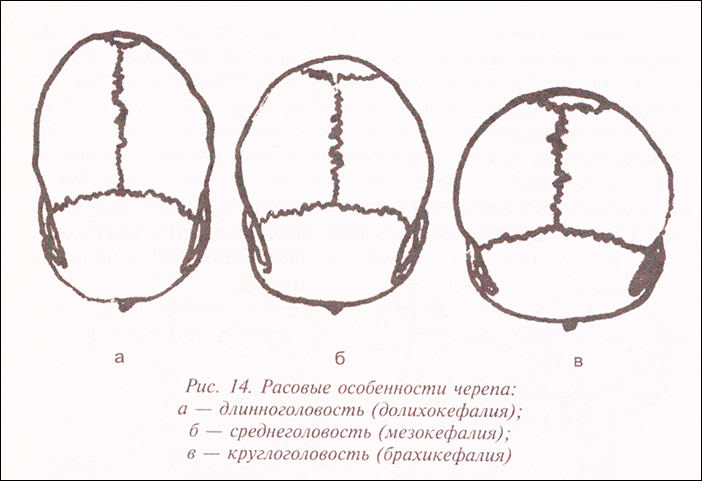
RACIAL FEATURES OF THE SKULL
Racial features of the skull: long-headed (dolichocephaly), medium-headed (mesokephaly), round-headed (brachycephaly).
SCIENTISTS HAVE FOUND GENES THAT CONTROL THE SIZE OF THE HUMAN SKULL
Geneticists have discovered five regions in human DNA that directly determine the maximum size of the skull and affect intellectual development and susceptibility to certain brain diseases, according to an article published in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Back in the 19th century, scientists noticed that the shape and volume of the skull differed markedly for different individuals and even groups of people, which some unscrupulous individuals tried to use to justify various theories of racial superiority. In fact, as hundreds of more recent studies show, there is no connection between skull shape, cranial volume and intelligence.
Today, differences in the volume of the skull are of interest to neurophysiologists and geneticists for the reason that the genes responsible for its structure and size may be associated with or influence the development of various neurodegenerative diseases and give rise to specific features of individual development.
A huge team of geneticists, including scientists from Russia, conducted the first large-scale study of this kind, in which they tried to identify genes and DNA sections associated with the volume of the human skull. These experiments were carried out as part of the CHARGE and ENGIMA projects, aimed at searching for features in the structure of genes that affect the functioning of the heart and brain.
To do this, scientists extracted and analyzed the DNA structure of over 32 thousand inhabitants of Europe, Asia, Africa and the New World, after which they compared sets of small mutations in them and compared the data obtained with how different the volumes of their skulls were.
This comparison showed that the size and shape of the skull is determined by about 25% genetically, and that there are seven regions in our DNA, two of which were previously known to scientists, that are responsible for the volume of the skull. These genome fragments are located in our DNA in a fairly compact manner and they are located on chromosomes 6, 10, 12 and 17.
Interestingly, four of these new areas were previously associated not with the volume of the skull, but with human height. This prompted the scientists to conduct additional testing, which showed that the areas they discovered were not directly related to height and had the same effect on the size of the skull in both tall and short people.
On the other hand, they have been associated with head circumference in childhood, as well as mental abilities in childhood and adulthood, as well as susceptibility to Parkinson's disease, microcephaly and other serious diseases. Scientists do not yet know how exactly they are related to each other, but they plan to find out through larger genetic studies.
Many of these regions, geneticists explain, are located within genes that control cellular metabolism and tissue growth, which may explain why they simultaneously influence both skull size and mental abilities. Their further study, as the authors of the article hope, will help to understand how the volume of the skull can affect various aspects of human life and development.
The proposal of American geneticists to abandon the term “race” in scientific publications is being discussed by Russian scientists.
Are races not needed in modern genetics?
Women of the Ethiopian Hamar tribe. (Photo by Anders Ryman/Corbis.)
The Han people are the largest ethnic group in China and on Earth. (Photo by foto_morgana / https://www.flickr.com/photos/devriese/8738528711.)
Indian from Mexico. (Photo by Darran Rees/Corbis.)
Recently in the magazine Science An article was published on the scientific concept of the human race. Authors of the article, Michael Udell ( Michael Yudell) from Drexel University in Philadelphia and his colleagues from the University of Pennsylvania and the Museum of Natural History believe that the term "race" does not have a precise meaning in modern genetics. And if you consider what problems have arisen and are arising around race, is it not better to abandon them altogether?
Historically, the concept of “race” was introduced to designate and describe the phenotypic differences of different people (skin color and other characteristics). Nowadays, some biologists continue to consider races as an adequate tool for characterizing the genetic diversity of human populations. In addition, racial disparities must be taken into account in clinical research and in the practice of medicine. But Michael Yudell and his colleagues are convinced that at the current level of development of molecular genetics, the term “race” cannot accurately reflect genetic diversity. In their opinion, this is how we artificially divide humanity into hierarchically organized groups. Race is not a clear biological marker, since races are heterogeneous, and there are no pronounced barriers between them.
The authors of the article also object to the use of this term in medicine, since any groups of patients united by race are genetically heterogeneous due to mixing and miscegenation. To support this, some examples from medical genetics are given. Thus, hemoglobinopathies (diseases caused by deformation and dysfunction of red blood cells) are often misdiagnosed due to the fact that they are considered black diseases.
Cystic fibrosis, on the other hand, has “unluck” in African populations, as it is considered a disease of whites. Thalassemia also sometimes escapes the attention of doctors, who are accustomed to seeing it only in the Mediterranean type. On the other hand, misunderstandings of the term “race” fuel racist sentiments that scientists have to respond to. Thus, in 2014, a group of population geneticists on the pages New York Times came out with a refutation of the fact that social differences between races are associated with genes.
To avoid all these problems, instead of using the term “race,” we could use “ancestry” and “population” to describe groups formed by genetic characteristics. Many people seem to agree with the authors of the article - in particular, an organization called The U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine is planning to organize a meeting of experts in biology, social sciences and humanities, in order to find new ways to describe the diversity of humanity instead of “races”, suitable also for laboratory and clinical research.
Opinions of Russian scientists
Article in Science prompted both anthropologists and geneticists to speak out. Thus, anthropologist Leonid Yablonsky believes that the “anti-racial campaign” does great harm to science and is reminiscent of the times of Lysenkoism in the USSR. By the end of the 20th century, a situation had developed in the United States that any anthropologist who spoke about the existence of races was ostracized and accused of racism. Mentioning race is considered rude in the scientific community.
However, according to Yablonsky, by denying race, we not only fall into scientific error, but at the same time give way to purely racist fabrications. As for the authors of the article in Science, then they are apparently simply incompetent in the subject they are writing about. (There may be some truth to this, since only one of the paper's co-authors, Sarah Tishkoff ( Sarah Tishkoff), is a specialist in population genetics.)
The same objections can be heard from anthropologist Stanislav Drobyshevsky, who emphasizes that the authors do not mention a single specialist in racial studies and do not provide a clear definition of race. Most importantly, they do not understand that, since the 20th century, race has been defined exclusively for the population, and not for the individual.
However, there are other opinions. For example, anthropologist Varvara Bakholdina says she largely agrees with this point of view, as she is also concerned about the indiscriminate use of the term “race” in scientific literature. In her opinion, today this term is not adequate to the current situation in science, and therefore I would like the anthropological classification to be based not on traditional racial diagnostic characteristics, but on a genetic database.
But it is genetics that tells us that races really exist. They, in particular, can be seen on genogeographic maps used to study the genetic variability of populations, as Oleg Balanovsky writes about in his recently published book “The Gene Pool of Europe”. Using such maps to study the fate of ancestral genetic components, we see that people are first divided into three large races - Negroids, Caucasoids and Mongoloids, and with increasing resolution the Americanoid and Australoid races appear.
“It is amazing and sad that with such complete confirmation of traditional racial classifications by the latest genetic data, there is still a widespread belief that genetics has ‘proved’ the absence of races,” concludes O.P. Balanovsky. Population geneticist Elena Balanovskaya wrote about this back in 2002: “The widespread belief that genetics (and especially molecular genetics) has provided important counterarguments against racial classifications is nothing more than a myth.”
Race is a biological concept, not a social one.
Anthropologist and paleontologist Evgeniy Mashchenko also largely disagrees with the authors of the “anti-racial” article, and above all with the fact that historically the concept of “race” was introduced to designate and describe phenotypic differences between different people. Mashchenko recalls that the term “race” was introduced into scientific circulation by Francois Bernier in 1684 to designate groups of people living in different regions of the Earth: a single biological species Homo sapiens breaks up into local groups with a certain geographical distribution, called races (from the Latin razza- tribe).
In the animal world, human races correspond to subspecies. Racial characteristics are inherited, although they are quickly eroded during the direct mixing (message) of races with each other. The main subject of debate among experts was the connection of certain characteristics with the specific geographical area of each race/population. In the 21st century, this connection is manifested quite weakly, but 300-500 years ago it was very clearly visible.
In Russian anthropology, traditionally since the end of the 19th century, the concept of race was based primarily on its BIOLOGICAL understanding. Homo sapiens is a single species that, in the course of its history, has adapted to different environmental conditions. Racial characteristics are considered as adaptive changes that occur in groups that have been under the influence of various external factors for a long time.
Differences between different human populations began to appear no earlier than the end of the Paleolithic era (50-40 thousand years ago), when people actively settled in new territories, and such differences arose in response to specific living conditions in modern-type geographic zones. (Before, that is, until the end of the Paleolithic, people did not have such population differences, or we cannot say anything reliable about them.) Human populations had to adapt to different amounts of sunlight, different proportions of microelements in food, to different diets that differed from region to region, etc. Characteristic features of races/populations, such as skin color or “invisible” biochemical characteristics, were finally established in the historical era, with the emergence of developed social societies and the transition to a productive economic system.
For races to form, human populations had to be socially or geographically isolated from each other. But races can change, and their changes are especially noticeable in the modern era. Over time, the development of technology and the spread of cultural traditions common to huge groups of people made geographic and social isolation almost impossible.
It should also be taken into account that the majority of humanity, thanks to scientific and technological progress, no longer experiences such a strong influence of environmental factors, so that racial differences due to their influence are gradually blurred. This is quite rightly noted by the authors of the article in Science. However, their further reasoning cannot be considered correct, since they do not at all consider a large amount of information about adaptive biochemical and physiological differences that persist in different groups of the Earth's population today.
These differences are well known even to those not involved in science. For example, everyone knows that part of the population of Northeast and East Asia has increased activity of alcohol dehydrogenase, an enzyme necessary for the utilization of alcohol; and that in the adult population of southern and central China (as well as in a number of other groups of people), the enzyme that breaks down the main milk sugar, lactose, does not work.
Let us repeat once again that the concept of race is biological, not social, that it explains the reasons for the differences between different groups of people in the past. The racism that frightens everyone has nothing to do with the scientific content of the concept of “race,” and it is not clear why science should suffer due to social or political ambiguous uncertainties.
Races—groups of people with clearly distinguishable characteristics—have long symbolized numerous attempts to divide people into lower and higher categories. Until recently, it was believed that the observed differences between races were due not to genetic, but to purely external reasons, including social ones. But there is evidence that populations and races still differ from each other in DNA. That is, races are a genetic reality. But what then determines a person’s behavior - antisocial or non-traditional sexual orientation - special genes or upbringing?
“The DNA of all people, regardless of their skin color or hair texture, is 99.9% identical, so from a genetic point of view, the concept of race is meaningless,” says Sally Lerman in the pages of the authoritative Scientific American. According to this point of view, the observed differences between races are not due to genetic, but to purely external reasons, including social ones. “Research shows that the concept of race at the genetic level is nonsense,” she continues. “Races are subject to change, both geographically and historically. ... By placing too much emphasis on DNA, we turn a health problem into a biological one.” "inevitability. There is also a great temptation to use the same tool when talking about the genetic basis of criminal tendencies or intelligence."
Races are a genetic reality
In general, the conclusion about the great influence of living conditions on personality development in different ethnic and racial groups is correct. However, genetic differences do exist. Moreover, we undertake to assert that populations and races differ from each other in DNA - this is the subject of a commentary (provided by the editors from the June issue of “In the World of Science”) by Lev Zhivotovsky2, professor, doctor of biological sciences.
One can completely agree with most of its (Sally Lerman's article) provisions. Indeed, the concept of race, as a group of people with clearly distinguishable morphological characteristics, has long become a symbol of the division of people into lower and higher categories. Differences between races in hair pigmentation, skin and related characteristics in recent centuries have become the basis of the thesis about the biological inequality of people.
Eugenics and psychology, relying on testing data (intellectual development coefficient IQ), tried to prove the genetic nature of racial inequality. However, population genetics has shown the inconsistency of this view. It turned out that the differences between members of the same race far exceed the differences between races. And recently it was found that people of even different races differ from each other in DNA less than different individuals of chimpanzees in the same herd. However, we are not identical genetically (only identical twins have almost the same DNA) - we are all slightly different from each other.
Sally Lerman argues that the observed differences between races are not due to genetic factors, but to purely external factors, including social ones. In general, the conclusion about the great influence of living conditions on personality development in different ethnic and racial groups is correct. However, genetic differences also exist. Based on data from recent years, we undertake to assert that populations and races still differ from each other in DNA. But their genetic difference in itself cannot serve as a measure of the hereditary inequality of people of different origins. Genetic differences between populations and races are not biological inequality: they arose evolutionarily and are capable of evolutionary change.
“The DNA of all people, regardless of their skin color or hair texture, is 99.9% identical, so from a genetic point of view, the concept of race is meaningless.”
The argument given against the existence of genetic differences between races is not really an argument. Indeed, the human genome consists of three billion nucleotides (more precisely, they speak of pairs of nucleotides, because DNA consists of two complementary chains). Therefore, 99.9% match, or 0.1% difference, means that people differ from each other in three million base pairs. Probably, most of these differences occur in informationally “silent” regions of the genome, but the remaining functionally significant differences are sufficient to ensure the individuality of each of us. It is known that the DNA of humans and chimpanzees coincides by 98-99% - this figure is also large at first glance. However, humans and chimpanzees are different zoological species, separated by at least five million years since their evolutionary lineages separated from a common ancestor.
“Research shows that the concept of race at the genetic level is nonsense.”
Now we can say that this is not so - the indicated three million nucleotide pairs are enough to cause genetic differences between races. Recently, more than fifty native populations from different regions of the world (South Africa, Western Eurasia, East Asia, Oceania, America) were examined at almost four hundred genetic loci of various genome regions3-4. These geographic population groups correspond to the main human races (the term “race” was not used in these publications, since over many decades it turned out to be emotionally overloaded and evokes associations that are far from scientific). It turned out that among these loci there are no ones that would clearly “mark” one or another race. However, for each of them, an interracial difference that was practically indistinguishable by statistical methods was revealed. These tiny differences were accumulated by all four hundred loci until complete racial identification - according to the genetic “profile”, each individual could be unambiguously assigned to one of the geographical groups.
"Races are subject to change, both geographically and historically."
The above data confirms this conclusion: statistically significant differences were found between populations (ethnic groups) from the same geographic region (same race). However, these differences were not one hundred percent: an individual could not always be unambiguously assigned to one or another population1. The differences themselves between geographic groups and between populations within a region evolved evolutionarily over many tens of thousands of years under the influence of mutations and population genetic processes, and the degree of difference corresponded to the time that passed after humans left Africa and settled across different continents.
The time of genetic isolation between regions was sufficient for the accumulated genetic differences between them to become identificationally significant. However, the division of populations within the region occurred much later, and therefore there was not enough evolutionary time for the development of significant differences within the region. True, this does not exclude the possibility that the involvement of, say, several thousand loci in the analysis accumulates additional differences and makes it possible to identify populations within a race. Mass migrations, interracial marriages and miscegenation can quickly, within a few generations, destroy evolutionarily established genetic differences. This suggests that race, although real, is not a frozen category that does not absolutely separate people according to biological characteristics. Race, like ethnicity, is a historical, evolutionary concept.
This is confirmed by another fact. In terms of DNA, we are quite close to the Neanderthal, much closer than to the chimpanzee, but we represent different evolutionary branches that diverged from a common ancestor much earlier than the human races from each other - about 500-700 thousand years ago. For the purposes of this discussion, we and Neanderthal man are simply very different races that have reached the status of subspecies of Homo sapiens: according to modern nomenclature, we are Homo sapiens sapiens, and Neanderthal man is Homo sapiens neanderthalensis. However, the genetic differences between modern human races are much smaller, than the differences between us and Neanderthal man.
"Race exists at least as a factor of distinction from a medical point of view. One cannot abandon this concept without abandoning along with it all the epidemiological data known to date." The different prevalence of hereditary pathologies in different races is also associated with evolutionary processes. Hereditary diseases arise as “harmful” mutations—“breakdowns” of functionally important genes, which are then passed on to descendants if the carriers of such mutations survive to reproductive age. Therefore, a certain mutation, if it does not disappear, spreads mainly among close populations and further through migration. Thus, based on a purely random process of the appearance of harmful mutations, regional differences in certain hereditary pathologies arise over time. This process leads to differences in the spectrum of hereditary diseases not only between races, but also between populations within a race. Of course, the prevalence of a particular hereditary disease can be restrained or, conversely, enhanced by specific environmental factors. And in this sense, we can agree with the author’s phrase: “Race is part of the environmental background of the human genome.”
"By placing too much emphasis on DNA, we turn a health problem into a biological inevitability. There is also a great temptation to use the same tool when talking about the genetic basis of criminal tendencies or intelligence."
These fair phrases touch on the most important problem: how the contributions of genes and environment relate to the development of the characteristics and characteristics of each person. Is antisocial behavior or non-traditional sexual orientation really determined by special genes or is it due to upbringing? It has now become fashionable to refer to the genetic fatality of today's expanding extreme manifestations of personality. However, there is no serious evidence for this, except in cases where marginal behavior is caused by serious hereditary defects. On the contrary, there is a large number of facts confirming the leading role of perception, imitation and motivation in the development of personal characteristics.
"Race is something like kinship."
One might add “evolutionary” or “genetic” kinship.
Lev Zhivotovsky, CNews
(Samuel Jared Taylor about the book Philip Rushton "Race, evolution and behavior")
"Race, evolution and behavior" is a book of rare importance on the question of race. It not only describes the countless differences between the races, but also explains in a fresh and compelling way what these differences mean and what causes them. Professor J. Philip Rushton from the University of Western Ontario wrote a strictly scientific work, which is difficult to understand in places, but is quite capable of becoming a classic in its field, like the works " Race"John Baker and" Bias in intelligence testing"Arthur Jensen.

How different are the races? Today, most experts accept differences in intelligence as a given. Professor Rushton went much further and classified a large amount of data into other important distinctions. Some of them are summarized below in a table that deserves careful study. The most striking discovery is not that Asians, whites, and blacks are different from each other, but that these differences constitute a spectrum, with blacks and Asians at the ends of the spectrum, with whites in between.
Much of the book - and our article - is devoted to reviewing these data, but Professor Rushton's boldness and innovation were most evident in his correlation of the range " asians-white-black"with the r-K selection theory.
The r-K selection theory is outlined in the figure below.
Through evolution, different species have developed different approaches to reproduction. At one end of the scale is r-strategy: organisms that follow it produce very numerous offspring, but either take little or no care of them. A good example is the oyster. Every year it releases millions of larvae into the ocean, leaving them to the mercy of the elements and predators. Almost all of them die, but some survive.

Oysters are typical r-strategists. They produce 500 million fertilized eggs per year and do not show any parental care about them. Large apes are typical K-strategists. They give birth to one young every five to six years and care for it tenderly.
r-organisms are forced to reach maturity quickly because they are deprived of parental help. Those that survive repeat the cycle, also producing millions of larvae, of which only a few will survive. Symbol " r" means the maximum rate of population growth - when conditions for reproduction are favorable, the r-strategist multiplies at a frantic pace.
At the other end of the scale is K-State, which is followed by most higher vertebrates, including humans. Their offspring are much smaller in number, but the parents carefully look after each offspring and thereby significantly increase its chances of survival. Accordingly, K- and r-strategists are very different both biologically and, in the words of Prof. Rushtona - " biographically".
K-strategists live longer, have larger brains, and reach puberty more slowly. Unlike more primitive r-strategists, they are characterized by a certain social organization. In addition to caring for their young, adults can also share food, hunt together, and fight off predators. Symbol " TO" means the maximum population density and represents the production of a few offspring, which are carefully prepared for life in a certain habitat.
People are typical K-strategists. Their offspring are few in number, take a long time to mature and require careful care. They have large brains and a complex social organization based on cooperation. Yet the human races are not the same. The table below shows that Asians exhibit K behavior more than whites, and whites more than blacks. There are almost no exceptions to this model.
Comparative ranking of races by r-K indicators
|
variable |
Mongoloids |
Caucasians |
Negroids |
|
brain size |
biggest |
intermediate |
the smallest |
|
IQ score |
105 |
100 |
85 |
|
decision time |
fast |
average |
slowly |
|
cultural achievements |
high |
high |
low |
|
duration of pregnancy |
? |
average |
short |
|
biological maturation |
the latest |
intermediate |
at the earliest |
|
age of first sexual intercourse |
latest |
intermediate |
the earliest |
|
life expectancy |
greatest |
intermediate |
smallest |
|
number of fraternal twins per 1000 births |
4 |
8 |
16 |
|
sex hormone levels |
lowest |
intermediate |
highest |
|
genital size |
the smallest |
average |
biggest |
|
frequency of sexual intercourse |
smallest |
average |
highest |
|
sexually transmitted diseases/AIDS |
low level |
average level |
high level |
|
aggressiveness |
lowest |
average |
the tallest |
|
caution |
the tallest |
average |
lowest |
|
leadership |
lowest |
average |
the highest |
|
self-esteem |
lowest |
average |
the tallest |
|
family stability |
the tallest |
average |
lowest |
|
crime |
lowest |
average |
the tallest |
|
administrative abilities |
the highest |
average |
the lowest |
Sexual maturity and reproduction
Racial differences in reproductive psychology are almost entirely consistent with the r-K model, with blacks and Asians at the poles and whites in between.
For example, a fraternal pregnancy, which occurs when more than one egg is released from the mother's ovary during ovulation, is a typical r-strategy aimed at producing more numerous and smaller offspring. Such conceptions are more likely to end in miscarriage, and twins are more likely to be born premature, more likely to die in infancy, or receive less parental care.
Blacks are twice as likely to have fraternal twins as whites, and whites are twice as likely to be born to Asians. Triplets occur ten times more often in whites than in Asians, and in Africans seventeen times more often than in whites. In some African populations, there are 60 multiple births per 1000 births. In Japan, where twins are rare, they are viewed with suspicion and called " litter", believing that this is more characteristic of dogs than of humans.
The timing of pregnancy and puberty in different races also corresponds to different r-K strategies. Thus, blacks are born earlier than whites and are smaller than the latter, but they are stronger and have better coordination. They begin to sit up and roll over earlier than whites, who, in turn, learn to do this earlier than Asians. On average, blacks begin walking at 11 months, whites at 12, and Asians at 13 months of age.
Africans erupt molars earlier than whites, and Asians later than others. Among primates in general, there is almost complete correspondence between the timing of molar eruption and life expectancy, brain size, timing of puberty, and the complexity of social structure.
Blacks reach puberty earlier than whites, and whites earlier than Asians. By age 12, fully developed breasts and pubic hair are observed in 19% of black American women and only 5% of white women. On average, blacks experience their first period earlier than whites, and whites earlier than Asians. In the United States, white women become sexually active on average two years later than black women, and Asian women even later than white women.
Professor Rushton was not afraid to touch upon the sensitive issue of the size of the genitals, which, due to the spread of AIDS, although reluctantly, is still being raised at the official level. International organizations that aim to provide condoms to people around the world have concluded that a standard size does not suit everyone. Blacks have larger penises than whites, and whites have larger penises than Asians. The depth of the vagina also varies among different races. Black men produce more seminal fluid than white men, and Asian men produce the least.
The highest frequency of sexual intercourse in the United States is observed among black couples, the lowest among Asian couples. AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases are most common among blacks and least common among Asians.
For Africa, compared to Europe and Asia, multiple sexual relationships are more typical, and care for children is less pronounced. Often older siblings look after younger children. There are also huge racial and geographic differences in offspring numbers. The average North American woman produces 14 children, grandchildren and great-grandchildren - in Africa the number is 258. Corresponding to this amazing African fertility is a shorter life expectancy. Blacks live less than whites, who in turn live less than Asians.

All differences in the timing of reaching maturity and reproductive behavior fit perfectly into the r-K theory scheme. Early maturity, early reproduction, numerous offspring, shorter life - all this allows blacks to be placed closer to " oyster" end of the r-K range than whites, who, in turn, are also closer to it relative to Asians.
Differences in sexual activity, life expectancy and number of children are usually explained by " culture" or " surroundings", however, there is every reason to believe that they are - at least in part - due to heredity. At the same time, the size of the genital organs and the age of puberty almost entirely determined by genetics.
Life expectancy is undoubtedly partly due to heredity.
The age at which an adopted child will die will be more accurately predicted based on the life expectancy of his biological - rather than his adoptive - parents. It is also known that identical twins die at an average interval of only 3 years and 1 month, while for fraternal twins this interval is 6 years and 6 months.
What about such components of the K-strategy as altruism, law-abidingness, and other characteristics characteristic primarily of human social organizations? To what extent is what we call " character" - as well as cultural institutions that reflect the group nature of the population - are determined by genetics and, accordingly, can be included in the analysis of the r-K strategy? Professor Rushton studied in detail modern research on heredity, and came to the conclusion that genetics has a powerful influence on literally every aspect of humanity behavior.
Heredity and environment
The most impressive and convincing evidence of the comparative influence of heredity and environment comes from the study of identical twins who were separated after birth and raised in different families. Identical (monozygotic, identical) twins develop from one egg after it divides into two; such twins are genetically identical. Fraternal twins develop from two fertilized eggs and are no more genetically similar than ordinary brothers or sisters. (Rates of births of identical twins, as opposed to rates of births of fraternal twins, across races is the same).
A discovery of extraordinary importance was that identical twins, when raised in different families, are more similar to each other in literally every way than fraternal twins raised in the same family. Based on these similarities, it seems possible to assess the proportion to which heredity and environment are responsible for differences in personality traits.

The data in the following table comes from a study of twins. These are estimates of how genetically determined different aspects of the human worldview are. These figures almost certainly underestimate the role of heredity, because the method used to calculate them assumes that a person's environment is completely random. In fact, people influence their own environment to a very large extent due to character traits that are partly inherent in them from birth. Thus, an aggressive child evokes a completely different reaction from parents and playmates than his quiet and sympathetic brother or sister, and thereby creates a different environment for himself. And having become independent from their parents, young people begin to follow their innate inclinations to an even greater extent, thus creating for themselves a completely different environment.
The method for estimating heritability ignores these facts. After all " environment", which influences personality traits, largely represents the personal environment, which varies from person to person primarily because people themselves form it depending on their genetic preferences.
Assessment of the hereditary component in relation to:
|
Death penalty |
|
|
Royal family |
|
|
apartheid |
|
|
White supremacy |
|
|
Divorces |
|
|
Keeping the Sabbath |
|
|
White lies |
|
|
Mixed marriages |
|
|
Legal abortion |
|
|
Nudist camps |
|
|
Socialism |
|
|
Learning Latin |
|
|
Computer music |
|
|
Bible truths |
|
|
Children's sleepovers |
|
|
Co-education between the sexes |
Intelligence, one of the most important, most stable and frequently measured characteristics, is also one of the most genetically determined. Differences in intelligence within a population are determined by heredity by 60-80%.
It is important to note that what is being assessed here is difference IQ, not IQ in general. Let's say two brothers have IQs of 100 and 120, and IQ is determined 60% by genes (and another 40% by environmental influences). This does not mean that 40 out of 100 intelligence points in the first brother are determined by the environment. This only means that non-genetic reasons could, in theory, account for 40% of the 20-point difference between the intelligences of brothers - that is, 8 IQ points.
In addition, we do not know how environment influences the remaining 40-20%, which is presumably not genetic. Non-genetic causes may in fact be such clearly biological factors as malnutrition, childhood illnesses, intrauterine injuries, and not the household or educational differences that most people understand by " environment"Programs like Head Start or remedial education do not have any long-term effect on differences in intelligence between individuals or races.
Professor Rushton summarized the results of a number of studies of intelligence in different racial groups and derived the following averages:
white - 100
Asians - 105
black Americans (who are about 25% white) - 85
black Africans - 70 -75
American Indians (including Central and Latin Americans with little or no European blood) - 89
Polynesians, Micronesians, Melanesians and Maoris - 80 -95
Although Asians generally have higher intelligence than whites, this difference is observed primarily in the visual-spatial domain rather than in verbal abilities. Therefore, Asians are good engineers and mathematicians, but they do not have a pronounced advantage in professions such as law or language teaching. Not surprisingly, a 1980s study of the US profession found that the share of Chinese Americans in science was six times greater than their share of the national population. At the same time, Chinese lawyers accounted for only a quarter of their share of the population. Blacks were poorly represented in both areas.

Intelligence tests are commonly criticized for producing disparate results based on race. However, there are other, completely biological indicators of the level of intelligence that cannot be blamed on " cultural bias"Professor Rushton personally studied one of these signs - brain size.
A larger head size (and thus a larger brain) is positively correlated with intelligence. We see this in families where the brother with the biggest head is likely to be the smartest. We see the same thing within races: Blacks and Asians with large brains are more likely to be smarter than their smaller-brained counterparts.
When comparing racial groups, it appears that whites and Asians have larger brains than blacks. Thus, at age seven, black children are 16 percentile taller than white children, but their head circumference is 8 percentile smaller. Asians are more likely to have larger brains than whites, although sometimes this superiority is only apparent after adjusting for the fact that Asians have smaller bodies than whites. A petite person with the same brain size as a large person can be said to have a "larger" brain because a petite body requires a smaller brain to maintain basic functions.
The brains of whites contain on average 100 million fewer neurons than the brains of Asians, and blacks have 480 million fewer neurons than whites. The difference between blacks and Asians is all the more significant because of the differences in their body sizes. Blacks with small brains and large bodies are seriously inferior to Asians in intellectual terms, because they work to maintain basic functions. O the largest part of their already small brain, which therefore becomes inaccessible to thinking.
Another directly physiological method for assessing intelligence is the reaction time test, developed by prof. Arthur Jensen from the University of Berkeley. These tests require subjects to make a simple choice when a light comes on. Intelligence correlates with both reaction speed and consistency, with Asians outperforming whites and whites outperforming blacks.
Prof. Rushton provides a number of additional arguments that indicate that racial differences in intelligence are a function of genetics rather than environment. The first phenomenon is called reversion (or regression) to the mean. Individuals at the extremes of the normal distribution of any trait will produce offspring in which that trait will no longer be expressed to such an extreme degree. For example, very tall people will typically have children who will be taller than average, but their height will tend toward the population average. The same goes for intelligence: Research shows that black Americans return to an average of 85, while white Americans return to an average of 100.
Further compelling evidence that racial differences in intelligence are genetically determined is inbred (or inbred) depression. Children born from unions between very close relatives often score unusually low on certain types of intelligence tests. This suggests that the abilities these tests measure are highly dependent on genetics. Interestingly, these are precisely the intelligence tests in which the differences between blacks and whites are most pronounced, which means that this intellectual gap is also determined by heredity.
Other personality differences
High intelligence is not the only distinguishing feature of the K-strategy.
Prof. Rushton explains that races with more K-characteristics form more complex and cooperative social organizations, are more reserved and law-abiding, and exhibit greater altruism. According to the r-K theory, altruism and social cooperation allow individuals to raise their offspring in a more secure and peaceful environment, a necessary condition for groups whose survival depends on a small number of large-brained offspring that are slow to reach sexual maturity.
To have reason to include features such as altruism And aggressiveness , it is necessary to prove that they, like intelligence, are at least partly governed by heredity and differ from race to race. Research shows that these traits are highly influenced by heredity and that they appear early in life. One study notes that children who are perceived by their peers as " aggressive"assessed at 8 years of age were assessed in exactly the same way 10 years later by a different group of peers. By age 19, those who were classified as the 'aggressive' group were three times more likely to be in trouble with the law than those who were not considered" aggressive."
Identical twins are approximately twice as similar in altruism and aggression as fraternal twins. Research in Europe and Japan confirms that when one twin is convicted of a felony, identical twins are two to three times more likely to have a prior criminal record than fraternal twins.
Shyness And sociability also appear very early in children and persist into adulthood. A study of identical twins raised apart has found striking similarities not only in their personalities, but also in their professions, marriage rates, clothing styles and behavioral patterns.
Research also shows that the criminal behavior of adopted children can be predicted more accurately based on the behavior of their biological - rather than adoptive - parents. Between approximately 21 and 30 years of age, the formation of an adult personality is completed, and the environment no longer influences it much.
Prof. Rushton notes that most people marry and form friendships with people who are genetically similar. People are looking for those who not only look, but also think alike. It has been proven that the longevity of a marriage depends on the genetic similarity of the spouses - in intelligence, appearance and other personality traits, which are controlled to some extent by genetics.
So it's not surprising that half-brothers make more similar friends than half-brothers. Further, young criminals - apparently having a genetic predisposition to crime - usually form friendships with youth with the same predisposition.
This well-documented human preference to associate with similar people is important for understanding race relations. Even very young children discriminate between races and exhibit racial preferences. Prof. Rushton writes that, apparently, ethnocentrism and " racism"are natural mechanisms that built into the genotype person.
Manifestations of altruism are also important for understanding race relations. In almost all species, the closer two individuals are genetically, the more willing they are to help each other. This behavior is evolutionarily justified if genes are considered the basic units of evolution. Genes for altruism are inherited by future generations in greater numbers of copies if they give rise to a personality trait that encourages an individual to help his close relatives survive.
Ants and bees are especially altruistic - they often die in large numbers when defending their colony - because they have an unusual reproductive mechanism in which workers inherit 75% of their common genes. Squirrels and monkeys recognize genetic strangers among their own kind and are more willing to help close relatives.
Male rhesus macaques are known to be sexually promiscuous, so their female's baby may be sired by a different father. However, in some unknown way they are able to recognize their own children and treat them with more affection than the offspring of others. (Biological relationship was determined using a blood test)

Belding's ground squirrels mate with many partners, and females produce litters that include both full sisters and maternal-only sisters. Despite the fact that both are born in the same womb and live in the same nest, full sisters fight less often and help each other more often than maternal sisters.

In the human world, adoptive parents - that is, genetic strangers - use violence against adopted preschool children 40 times more often than biological parents. In societies where open sex is common and fathers are uncertain about their own paternity, they are more protective of their sisters' children than their wives' children. A sister’s child is always a close relative, while the child of a sexually free wife may turn out to be a step-child.
Experiments with altruism confirm the obvious: people are more willing to help their own kind. External similarity is a good indicator of genetic similarity, and Prof. Rushton notes that racial solidarity can be seen as high-level nepotism. It also shows that it is often useless to look for any social or economic reasons in the interracial conflicts occurring everywhere on the planet. They are most convincingly explained by genetic similarity and the desire to preserve a common set of genes.
Interracial differences
Races consistently differ from each other in personality traits that can be classified according to the theory of r-K selection. They also differ in intelligence. Asians are more reserved, more cooperative, and less aggressive than whites; whites are more reserved and less aggressive than blacks. This classification holds regardless of whether subjects are assessed by personality tests or by peers. From early childhood, blacks are more excitable and more eager to subjugate others than whites; Black men are more likely to show off and behave in a defiant manner. Asians are the least likely to strive for leadership and are less excitable. Self-awareness and introspection become stronger the more pronounced the K-characteristics are.

Racial disparities in crime rates are well known, so there is no need to provide numbers. These differences are consistently observed in both multi- and monoracial societies. However, certain circles stubbornly reject any explanation of these causes from a genetic point of view, which is why ridiculous “environmental theories” are multiplying.
As noted by Prof. Rushton, earlier in the 20th century, all forms of deviant behavior in America's Chinatowns were so weak, despite the poverty, that these ghettos were considered refuge from crime. As for blacks, their isolation invariably breeds crime.
Despite fashionable talk about low self-esteem among blacks, they have a higher opinion of themselves than whites; and whites have a higher opinion of themselves than Asians. Asians are the most introverted and anxious; blacks are the least. This is reflected in suicide statistics: whites commit suicide at twice the rate of blacks, and Asians commit suicide at a higher rate than whites.
Mental instability statistics show a different trend. 240 out of every 100 thousand blacks are admitted to psychiatric hospitals, but only 162 out of every 100 thousand whites. It does not depend on poverty or wealth; No matter what class they belong to, blacks suffer from mental illness, drug addiction, and alcoholism at higher rates than whites. Asians, despite their introversion and anxiety, are the least susceptible to mental disorders.
Intraracial differences
Prof. Rushton notes that r-K selection theory can also explain differences between individuals belonging to the same race. In other words, members of the same race vary according to the same pattern that distinguishes different races. In both Europe and Africa, the following characteristics usually go together: large families, short lives, high sexuality, weak family ties and a high incidence of twins.
Mothers of fraternal twins were more likely than others to have an early first menstruation and a large family; their children (not even twins) were born underweight or died in infancy; they were promiscuous and had shorter life expectancies. Prof. Rushton discovered that fraternal twins in any society are more likely to be born to members of the lower than the upper classes.
One Swedish study found that girls who got their periods early were more likely to lie, skip class, and use marijuana than girls who got their periods late. Early puberty in the United States is correlated with promiscuity, out-of-wedlock childbearing, school dropout, crime, and other social problems. Early puberty appears to be heritable, in that daughters resemble their mothers.
If altruism is an important K-characteristic, then crime should be considered an extreme r-characteristic. In large populations, crime is accompanied by behavior that almost perfectly describes the differences between blacks and whites and whites and Asians, namely: large families, out-of-wedlock childbearing, low intelligence, early puberty, promiscuity, weak family ties, poor child care and short life.

On these grounds, Prof. Rushton suggests that the entire complex of differences in r-K characteristics is largely controlled by heredity and manifests itself both within races and within different classes of society. It is obvious that the most physiological r-K characteristics are strongly influenced by heredity. Prof. Rushton adds that physiology is closely related to many other forms of behavior that were previously considered independent of heredity, but, according to new data, are very strongly determined by it.
In general, we have good reason to believe that the patterns of behavior that distinguish both races and individuals are largely innate, consistently consistent with the r-K model, and immune to social " programs".
Prof. Rushton boldly develops the idea further. In our era of social mobility, when most inherited social advantages have disappeared, people succeed or fail in life largely due to their innate abilities. Children from wealthy families are usually smart and talented because they have inherited the qualities that made their parents wealthy.
However, as noted by Prof. Rushton, a child's IQ is a better predictor of his future social standing than his parents' social standing. When less intelligent children of wealthy parents begin to fall down the social ladder, they adopt the habits and values of their new class instead of maintaining those of the class into which they were born. Even the most K-oriented parents can give birth to an r-offspring, who, as they grow older, will increasingly manifest their genetic inclinations.
Prof.'s conclusions Rushton deals a serious blow to modern egalitarian dogma. Unfortunately, the usual reaction to his works boils down to completely wild accusations of some nefarious plans. In the October 20th issue of the magazine " Rolling Stone" in the article " Professors who preach hate" attempts are being made to brand the professor as “ rabid racist».
Undoubtedly, it is the haters of science and free inquiry who build societies that inevitably degenerate, as is happening to ours. Anyone who wants to understand the world as it is, and base his politics on facts and not on fantasies, cannot ignore this very important book.
S. Drobyshevsky: You understand everything correctly! There are no “Caucasian” or “Negroid” haplogroups in nature at all. Races were distinguished based on the external characteristics of modern people. Haplogroups are gene variants that occur in different morphological races with different frequencies. It’s just that some geneticists tend to either simplify the writing or do not understand what they themselves are writing. When a haplogroup is FREQUENTLY found among Caucasians, geneticists call it “Caucasoid.” When it is often found among some peoples, they can easily call it “Turkic”, “Indo-European” or “Finno-Ugric”. And this is completely nonsense, because linguistics is not directly related to races and genes at all. But it can be convenient. In short, what to say: “a haplogroup that is found with the greatest frequency among representatives of peoples speaking languages of the Ugric linguistic family compared to representatives of other peoples.” If a haplogroup is found in Central Africa, this means that it exists there and is just as “Negroid” as “Caucasoid”. And here some migrations can be done in both directions. And even more so it’s nonsense to attribute a certain specific skin color to the carriers of a certain haplogroup! Skin color is determined by a mass of genes that have their own history. Now in Africa the carriers of this haplogroup are black, why then did the haplogroup necessarily have to be brought by white people? And if the pre-Holocene movement of haplogroup carriers has somehow been proven, it is stupid to talk about skin color, because we really don’t know what it was like then. Before the Holocene, there were no modern Caucasians at all; this has been no secret for 50-60 years. With the same success we can talk about the migrations of the Slavs in the Middle Paleolithic. Some people say, however...
Letter to the Editor: Are dark-skinned South Asians Australoid? Or are Australoids only Negritos, Melanesians and Australian Aborigines, and South Asians are closest to Caucasians?
S.D.: Are dark-skinned South Asians Vietnamese and Javanese? Or Dayaks and Badjaos? Or semangs with aetas? It's not all the same thing. If the Vietnamese are with the Javanese, then they belong to the South Asian race of Mongoloids and are not much closer to the Caucasians than the same Melanesians; but then they themselves are in no way Australoids. If the Dayaks are from the Badjaos, then they are classically classified as Veddoids, although I personally have great doubts in this regard, but in any case they will be representatives of the Eastern Equatorial variant with some admixture of the South Asian race; they will belong to the Australoids in the broad sense (synonyms are eastern equatorials, Australo-melanezoids), but not to the Australoids in the narrow sense (these are only Australian aborigines). If you meant the Semang, Aeta and Andamanese, then these are the Negritos you mentioned, who definitely belong to the Australoids in the broad sense. None of those mentioned are any closer to Caucasians. Closer to Caucasoids are African blacks, representatives of the Ural race and some of the Western Mongoloids mixed with Caucasians - people of the South Siberian race.
Mr_Bison (forum paleo.ru) : Is it possible to say that genetic mixing of races does not have harmful consequences for the offspring and are there any exceptions (pygmies?)?
S.D.: We can absolutely say that there are no harmful consequences. This has been checked and rechecked a hundred times, in terms of the incidence of diseases, mental disorders, birth rates, children's performance in school, and so on. Moreover, the most diverse mestizos were studied: Negro-European of various varieties, Polynesian-Japanese-European, Japanese-Negro, Bushman-European, Mongoloid-European, Australian-European, Russian-Buryat, Russian-Kazakh, and so on and so forth. Nowadays, in general, a GOOD percentage of the world's population are mixed races of various variants. More than half the population of Central and South America, for example. Almost all are Mexican. But the pygmies are very weakly mixed. It is from them that the flow of genes comes to the blacks, but no one goes to live with the pygmies. Mixed races of blacks and pygmies are quite normal; this is a significant percentage of the population of Central Africa.
The fact is that races differ from each other very slightly, mainly in external characteristics, but not even at the level of subspecies. Actually, the difference between races and subspecies is that subspecies are usually well isolated from each other, but races are not isolated in any way; there are always transitional variants. And always, at all times, there was mixing. Therefore, there are no harmful consequences. It is not very long ago that the races arose and were never separated by sharp barriers.
Svetlana Borinskaya: There may be various effects. I haven’t looked at the articles on interracial offspring - you can ask anthropologists, but my geneticist colleagues have data on interethnic marriages. Children from interethnic marriages in Moscow (you need to look in more detail - this is the long-standing work of Yu.P. Altukhov) at birth had, on average, lower health indicators. According to the distribution, for example, weights often fell not into the middle of the bell-shaped weight distribution curve (which is optimal), but into the edges. The descendants of Russians and Selkups had, on average, higher cholesterol levels than Russians or Selkups (works by M.I. Voevoda, it seems). The reasons may be genetic ( Parents are adapted to different environmental conditions, but to which will the child be adapted?), and social - in interethnic marriages in Moscow, at least one spouse was most likely a newcomer, and newcomers may have less favorable social conditions.
Mr_Bison: Could you name, as an example, some differences in the phenotype of races that are not adaptive, but are caused, say, by the bottleneck effect and/or random mutations? Do these maladaptive differences outweigh the adaptive ones?
S.D.: Blonde hair in many groups is such an example. Light hair color does not seem to be adaptive or very weakly adaptive. And it arose many times independently: in northern Europe, in the North Caucasus, among the Kabyles in the Atlas Mountains, among the inhabitants of the Hindu Kush, among the Melanesians of the Solomon Islands, among the aborigines of Central and Northern Australia. Most likely, this brightening is associated precisely with the bottleneck effect on the scale of small isolated populations.
This is probably how epicanthus arose - the version that it protects the eye from dust, although widespread, does not stand up to criticism (a lot of groups live in dusty places without epicanthus - Bedouins, Arabs and Australians, for example - and the Mongoloids did not arise at all in dusty places).
The shape of the bridge of the nose is most likely also from this series, although it may be subject to the effects of sexual selection.
It's difficult to say what prevails. On the one hand, we may not know the adaptive value, on the other hand, we generally imagine a clear adaptive value for a very small number of traits. Moreover, one does not interfere with the other: the value may be so weak that the statistical effects of changes in gene frequencies may outweigh this value. In general, it is difficult to count the signs. Should hair color be considered as one sign or several, given that even black color is encoded differently in the genome of different people? Such calculations, by definition, will be speculative.
S.B.: There are plenty of neutral genetic differences between races. For example, the same haplogroups mtDNA or Y - (for individual haplogroups a connection with adaptive traits was assumed, but it seems that it was never proven).
Mr_Bison: Is it possible to say that when mixing races, the health of the offspring should, all other things being equal, increase rather than decrease, since the likelihood of the transition of harmful recessive genes characteristic of each race into a homozygous state and heterozygous advantage decreases (such as the HbSHbS mutation that protects against malaria or the CFTR that protects against cholera) has now almost lost its role while its harmful side effects in the homozygous state remain?
S.B.: It is forbidden. According to HbS characteristics, the majority of representatives of groups where malaria was rampant are heterozygous without additional effort. At the population level, interracial or interethnic marriages are not significant for reducing the frequency of homozygotes (there are already 1%-2% of them - not significant for the survival of the population, although significant for an individual family in which a sick child may be born).
There are many such works. For example,
Genetic structure of human populations.
Rosenberg NA, Pritchard JK, Weber JL, Cann HM, Kidd KK, Zhivotovsky
Within-population differences among individuals account for 93 to 95%
of genetic variation; differences among major groups constitute only 3
Mr_Bison: I have seen many times on the Internet the statement that the genetic distance between large races does not exceed 0.03 according to Masatoshi Nei, but unfortunately I have not found a credible source. Forum posts only. Is this really true? And is the genetic distance between subspecies according to Ney usually equal to 0.17-0.22?
S.B.: There are many such works. For example, Genetic structure of human populations.Rosenberg NA, Pritchard JK, Weber JL, Cann HM, Kidd KK, ZhivotovskyLA, Feldman MW.Science. 2002 Dec 20;298(5602):2381-5: Within-population differences among individuals account for 93 to 95%of genetic variation; differences among major groups constitute only 3to 5%.
Mr_Bison: Do I understand correctly that it is nevertheless impossible to talk about the effect of heterosis (increased viability of hybrids) when different races are mixed, since the races are too close to each other genetically?
S.B.: It is correct that the heterosis effect does not apply to interracial or interethnic marriages. The description of the reasons is incorrect. What is important is not the label of race or nationality, but the fact that living in an environment to which a person is not adapted has harmful consequences for offspring. And it is usually adapted to the conditions in which its ancestors lived. Members of different races (or ethnic groups) were adapted to different environments. The consequences for the offspring depend on how much the environment differs from the one to which the ancestors who passed on the genes were adapted.
For example, in Europeans, the e4 allele of the apolipoprotein E gene is associated with elevated cholesterol levels and occurs with a frequency of 5% to 15%. In Africans (allele frequency up to 40%), the e4 allele does not increase cholesterol levels, while in African Americans cholesterol is increased, but less than in Europeans.
In fact, over the past 10 thousand years, most people began to live in conditions other than those to which their ancestors were adapted - they stopped being hunter-gatherers. Genetic changes have occurred, but they cannot keep up with environmental changes - the environment is changing faster than genes. See the "thrifty genes" hypothesis in the article "Genes and food traditions." In interracial or interethnic marriages, a child may receive both the advantages of both parents and maladaptive characteristics. Therefore, from the point of view of genetics, the only question is that the environment and lifestyle correspond to the genotype.
Vasily (letter to the Editor; style preserved): COULD YOU ANSWER THE QUESTION: THE CRO-Magnons AND THEIR EASTERN CONTEMPORARIES PEOPLE FROM THE ASCENT HOME ARE EXTINCTION OR THERE ARE THEIR GENES IN MODERN EUROPEANS AND WHAT PEOPLES ARE SIMILAR TO THEM. AND HOW THEY DIED OUT IF STILL PEOPLE LIVE AS WELL AS MORE PRIMITIVE THAN THEM IN SKULL STRUCTURE. AUSTRALIANS FOR EXAMPLE.
S.D.: The question of the continuity of the Upper Paleolithic European Cro-Magnons and modern Europeans has two versions of the solution. Anthropology shows that Cro-Magnons are quite suitable for the ancestors of Mesolithic Europeans, and the latter - Neolithic, and those - modern people. Moreover, many modern groups in Europe are not fundamentally different from the Cro-Magnons and, apparently, are their more or less direct descendants - groups in Northern Europe, England, the Balkans, the Caucasus (taking into account all sorts of migrations and mixing, of course). But genetic data gives two versions. According to one, approximately 95% of modern Europeans are descendants of Cro-Magnons, the remaining 5% are descendants of Neolithic settlers from the Middle East, who brought agriculture, which the “Cro-Magnons” mastered. Surprisingly, other calculations by other geneticists show that 95% of modern Europeans are descendants of Neolithic settlers from the Middle East who brought agriculture, and the remaining 5% are descendants of Cro-Magnons, who were completely displaced by advanced migrants. How to understand such a difference in calculations is a question for geneticists. It seems that the very approach of calculating the percentage of locals and immigrants is erroneous. There was more than one migration and it did not happen all at once; some of the genes were initially common, some disappeared due to all sorts of genetic drifts, and some changed a lot. The problem is that geneticists analyze only modern DNA (and what kind of samples do they have??? did they look at everyone???), and draw conclusions about the Paleolithic and Neolithic. And this is wrong.
The question - which peoples are similar to the Cro-Magnons - does not make sense, because peoples are defined by social characteristics, and now no one hunts mammoths and no one sprinkles ocher on their burials. Anthropologically, many groups (NOT PEOPLES!) are similar, mainly on the periphery of Europe, which is logical in some ways. But the full set of Cro-Magnon traits cannot now be found in Europe, except in individual cases. It is clear that over 20 thousand years everything mixed up and changed several times; it would be strange to look for Cro-Magnons, even if Europe were an isolated island like Tasmania.
Australians are no more primitive than Cro-Magnons in terms of skull structure. What exactly is primitiveness? In a smaller brain volume? Then the Europeans are more primitive than the Cro-Magnons. Strong development of the brow? The Cro-Magnons had it too. In large teeth? The Cro-Magnons have no less. Primitiveness is generally determined by proximity to the ancestral state. Australians are no closer to some Heidelbergers than European Cro-Magnons. In general, the question of how the Cro-Magnons became extinct, if anyone is more primitive than them, seems strange. First of all, who said Cro-Magnons are extinct? Secondly, how could the population of Australia prevent or help a group in Europe become extinct? Stone Age globalization? Newts, coelacanths, and all sorts of foraminifera live now and do not die out because we are also on the planet. But here the difference in levels is much greater.
Question to Svetlana Borinskaya from the Editorial Board of the portal ANTHROPOGENES.RU: On October 8, the Rossiya-1 channel airs a film with the odious title “Genetics against Darwin.” In the announcement of the film, among several famous names, yours appears...
Once upon a time, in some corridor, when asked to comment on the ideas of some freak (that monkeys descended from humans), I replied that this was complete nonsense.
I was not informed that my interview would be included in a film called "Geneticists vs. Darwin." Naturally, I am not against Darwin. I am against scammers on television.