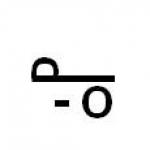This guide has been compiled from various sources. But its creation was prompted by a small book from the Mass Radio Library, published in 1964, as a translation of O. Kroneger’s book in the GDR in 1961. Despite its antiquity, it is my reference book (along with several other reference books). I think time has no power over such books, because the fundamentals of physics, electrical and radio engineering (electronics) are unshakable and eternal.
Units of measurement of mechanical and thermal quantities.
Electro units magnetic quantities
|
Relationships between units of magnetic quantities
in SGSM and SI systems
| In electrical engineering and reference literature published before the introduction of the SI system, the magnitude of the magnetic field strength N often expressed in oersteds (uh), magnitude of magnetic induction IN - in Gaussians (gs), magnetic flux Ф and flux linkage ψ - in Maxwells (μs). |
| 1e=1/4 π × 10 3 a/m; 1a/m=4π × 10 -3 e; 1gs=10 -4 t; 1tl=10 4 gs; 1μs=10 -8 vb; 1vb=10 8 μs |
| It should be noted that the equalities are written for the case of rationalized practical system ICSA, which was included in the SI system as an integral part. From a theoretical point of view, it would be more correct to O In all six relationships, replace the equal sign (=) with the correspondence sign (^). For example |
|
1e=1/4π × 10 3 a/m |
| which means: a field strength of 1 Oe corresponds to a strength of 1/4π × 10 3 a/m = 79.6 a/m |
| The fact is that units uh, gs And mks belong to the SGSM system. In this system, the unit of current is not fundamental, as in the SI system, but a derivative. Therefore, the dimensions of quantities characterizing the same concept in the SGSM and SI systems turn out to be different, which can lead to misunderstandings and paradoxes if we forget about this circumstance. When performing engineering calculations, when there is no basis for misunderstandings of this kind |
Non-system units
Some math and physical concepts
used in radio engineering
| Just like the concept of speed of movement, in mechanics and radio engineering there are similar concepts, such as the rate of change of current and voltage. They can be either averaged over the course of the process or instantaneous. |
|
i= (I 1 -I 0)/(t 2 -t 1)=ΔI/Δt |
| When Δt -> 0, we obtain instantaneous values of the rate of change of current. It most accurately characterizes the nature of the change in value and can be written as: |
|
i=lim ΔI/Δt =dI/dt |
| Moreover, you should pay attention - average values and instantaneous values can differ tens of times. This is especially clearly seen when a changing current flows through circuits with a sufficiently large inductance. |
decibel |
| To evaluate the ratio of two quantities of the same dimension in radio engineering, a special unit is used - the decibel. |
| K u = U 2 / U 1 Voltage gain; K u[db] = 20 log U 2 / U 1 Voltage gain in decibels. Ki[db] = 20 log I 2 / I 1 Current gain in decibels. Kp[db] = 10 log P 2 / P 1 Power gain in decibels. |
| The logarithmic scale also allows you to depict functions with a dynamic range of parameter changes of several orders of magnitude on a graph of normal sizes. |
| To determine the signal strength in the reception area, another logarithmic unit of the DBM is used - dicibels per meter. |
| P [dbm] = 10 log U 2 / R +30 = 10 log P + 30. [dbm]; |
| The effective voltage across the load at a known P[dBm] can be determined by the formula: |
 |
Dimensional coefficients of basic physical quantities
| In accordance with state standards, the use of the following multiple and submultiple units - prefixes is allowed: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Magnitude is something that can be measured. Concepts such as length, area, volume, mass, time, speed, etc. are called quantities. The value is measurement result, it is determined by a number expressed in certain units. The units in which a quantity is measured are called units of measurement.
To indicate a quantity, a number is written, and next to it is the name of the unit in which it was measured. For example, 5 cm, 10 kg, 12 km, 5 min. Each quantity has countless values, for example the length can be equal to: 1 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm, etc.
The same quantity can be expressed in different units, for example kilogram, gram and ton are units of weight. The same quantity in different units is expressed by different numbers. For example, 5 cm = 50 mm (length), 1 hour = 60 minutes (time), 2 kg = 2000 g (weight).
To measure a quantity means to find out how many times it contains another quantity of the same kind, taken as a unit of measurement.
For example, we want to find out the exact length of a room. This means we need to measure this length using another length that is well known to us, for example using a meter. To do this, set aside a meter along the length of the room as many times as possible. If it fits exactly 7 times along the length of the room, then its length is 7 meters.
As a result of measuring the quantity, we obtain or named number, for example 12 meters, or several named numbers, for example 5 meters 7 centimeters, the totality of which is called compound named number.
Measures
In each state, the government has established certain units of measurement for various quantities. An accurately calculated unit of measurement, adopted as a standard, is called standard or exemplary unit. Model units of the meter, kilogram, centimeter, etc. were made, according to which units for everyday use were made. Units that have come into use and are approved by the state are called measures.
The measures are called homogeneous, if they serve to measure quantities of the same kind. So, gram and kilogram are homogeneous measures, since they are used to measure weight.
Units
Below are units of measurement of various quantities that are often found in mathematics problems:
Weight/mass measures
- 1 ton = 10 quintals
- 1 quintal = 100 kilograms
- 1 kilogram = 1000 grams
- 1 gram = 1000 milligrams
- 1 kilometer = 1000 meters
- 1 meter = 10 decimeters
- 1 decimeter = 10 centimeters
- 1 centimeter = 10 millimeters
- 1 sq. kilometer = 100 hectares
- 1 hectare = 10,000 sq. meters
- 1 sq. meter = 10000 sq. centimeters
- 1 sq. centimeter = 100 square meters millimeters
- 1 cu. meter = 1000 cubic meters decimeters
- 1 cu. decimeter = 1000 cubic meters centimeters
- 1 cu. centimeter = 1000 cubic meters millimeters
Let's consider another quantity like liter. A liter is used to measure the capacity of vessels. A liter is a volume that is equal to one cubic decimeter (1 liter = 1 cubic decimeter).
Measures of time
- 1 century (century) = 100 years
- 1 year = 12 months
- 1 month = 30 days
- 1 week = 7 days
- 1 day = 24 hours
- 1 hour = 60 minutes
- 1 minute = 60 seconds
- 1 second = 1000 milliseconds
In addition, time units such as quarter and decade are used.
- quarter - 3 months
- decade - 10 days
A month is taken to be 30 days unless it is necessary to specify the date and name of the month. January, March, May, July, August, October and December - 31 days. February in a simple year - 28 days, February in leap year- 29 days. April, June, September, November - 30 days.
A year is (approximately) the time it takes for the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun. It is customary to count every three consecutive years as 365 days, and the fourth year following them as 366 days. A year containing 366 days is called leap year, and years containing 365 days - simple. One extra day is added to the fourth year for the following reason. The Earth's revolution around the Sun does not contain exactly 365 days, but 365 days and 6 hours (approximately). Thus, a simple year is shorter than a true year by 6 hours, and 4 simple years are shorter than 4 true years by 24 hours, i.e., by one day. Therefore, one day is added to every fourth year (February 29).
You will learn about other types of quantities as you further study various sciences.
Abbreviated names of measures
Abbreviated names of measures are usually written without a dot:
|
Weight/mass measures
|
Area measures (square measures)
|
|
Measures of time
|
Measure of vessel capacity
|
Measuring instruments
Special measuring instruments are used to measure various quantities. Some of them are very simple and designed for simple measurements. Such instruments include a measuring ruler, tape measure, measuring cylinder, etc. Other measuring instruments are more complex. Such devices include stopwatches, thermometers, electronic scales, etc.
Measuring instruments usually have a measuring scale (or scale for short). This means that there are line divisions on the device, and next to each line division the corresponding value of the quantity is written. The distance between the two strokes, next to which the value of the value is written, can be additionally divided into several smaller divisions; these divisions are most often not indicated by numbers.
It is not difficult to determine what value each smallest division corresponds to. So, for example, the figure below shows a measuring ruler:
The numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, etc. indicate the distances between the strokes, which are divided into 10 identical divisions. Therefore, each division (the distance between the nearest strokes) corresponds to 1 mm. This quantity is called at the cost of a scale division measuring device.
Before you begin measuring a value, you should determine the scale division value of the instrument you are using.
In order to determine the division price, you must:
- Find the two closest lines on the scale, next to which the values of the quantity are written.
- Subtract from greater value divide the smaller number and the resulting number by the number of divisions between them.
As an example, let’s determine the price of the scale division of the thermometer shown in the figure on the left.
Let's take two lines, near which the numerical values of the measured value (temperature) are plotted.
For example, bars indicating 20 °C and 30 °C. The distance between these strokes is divided into 10 divisions. Thus, the price of each division will be equal to:
(30 °C - 20 °C) : 10 = 1 °C
Therefore, the thermometer shows 47 °C.
Measure various quantities in Everyday life each of us has to do constantly. For example, in order to arrive at school or work on time, you have to measure the time that will be spent on the road. Meteorologists measure temperature, barometric pressure, wind speed, etc. to predict the weather.
Physical size called physical property material object, process, physical phenomenon, characterized quantitatively.
Physical quantity value expressed by one or more numbers characterizing this physical quantity, indicating the unit of measurement.
The size of a physical quantity are the values of numbers appearing in the value of a physical quantity.
Units of measurement of physical quantities.
Unit of measurement of physical quantity is a quantity of fixed size that is assigned a numerical value equal to one. It is used for the quantitative expression of physical quantities homogeneous with it. A system of units of physical quantities is a set of basic and derived units based on a certain system of quantities.
Only a few systems of units have become widespread. In most cases, many countries use the metric system.
Basic units.
Measure a physical quantity - means to compare it with another similar physical quantity taken as a unit.
The length of an object is compared with a unit of length, the mass of a body with a unit of weight, etc. But if one researcher measures the length in fathoms and another in feet, it will be difficult for them to compare the two values. Therefore, all physical quantities throughout the world are usually measured in the same units. In 1963, the International System of Units SI (System international - SI) was adopted.
For each physical quantity in the system of units there must be a corresponding unit of measurement. Standard units is its physical implementation.
The length standard is meter- the distance between two strokes applied on a specially shaped rod made of an alloy of platinum and iridium.
Standard time serves as the duration of any regularly repeating process, for which the movement of the Earth around the Sun is chosen: the Earth makes one revolution per year. But the unit of time is taken not to be a year, but give me a sec.
For a unit speed take the speed of such uniform rectilinear motion at which the body moves 1 m in 1 s.
A separate unit of measurement is used for area, volume, length, etc. Each unit is determined when choosing a particular standard. But the system of units is much more convenient if only a few units are selected as the main ones, and the rest are determined through the main ones. For example, if the unit of length is meter, then the unit of area would be square meter, volume - cubic meter, speed - meter per second, etc.
Basic units The physical quantities in the International System of Units (SI) are: meter (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), candela (cd) and mole (mol).
|
Basic SI units |
|||
|
Magnitude |
Unit |
Designation |
|
|
Name |
Russian |
international |
|
|
Electric current strength |
|||
|
Thermodynamic temperature |
|||
|
The power of light |
|||
|
Quantity of substance |
|||
There are also derived SI units that have their own names:
|
Derived SI units with their own names |
||||
|
Unit |
Derived unit expression |
|||
|
Magnitude |
Name |
Designation |
Through other SI units |
Through SI major and supplementary units |
|
Pressure |
m -1 ChkgChs -2 |
|||
|
Energy, work, amount of heat |
m 2 ChkgChs -2 |
|||
|
Power, energy flow |
m 2 ChkgChs -3 |
|||
|
Amount of electricity, electric charge |
||||
|
Electrical voltage, electrical potential |
m 2 ChkgChs -3 ChA -1 |
|||
|
Electrical capacity |
m -2 Chkg -1 Ch 4 Ch 2 |
|||
|
Electrical resistance |
m 2 ChkgChs -3 ChA -2 |
|||
|
Electrical conductivity |
m -2 Chkg -1 Ch 3 Ch 2 |
|||
|
Magnetic induction flux |
m 2 ChkgChs -2 ChA -1 |
|||
|
Magnetic induction |
kgHs -2 HA -1 |
|||
|
Inductance |
m 2 ChkgChs -2 ChA -2 |
|||
|
Light flow |
||||
|
Illumination |
m 2 ChkdChsr |
|||
|
Radioactive source activity |
becquerel |
|||
|
Absorbed radiation dose |
||||
ANDmeasurements. To obtain an accurate, objective and easily reproducible description of a physical quantity, measurements are used. Without measurements, a physical quantity cannot be characterized quantitatively. Definitions such as “low” or “high” pressure, “low” or “high” temperature reflect only subjective opinions and do not contain comparisons with reference values. When measuring a physical quantity, a certain numerical value is assigned to it.
Measurements are carried out using measuring instruments. There is quite a large number of measuring instruments and devices, from the simplest to the most complex. For example, length is measured with a ruler or tape measure, temperature with a thermometer, width with calipers.
Measuring instruments are classified: by the method of presenting information (displaying or recording), by the method of measurement (direct action and comparison), by the form of presentation of readings (analog and digital), etc.
The following parameters are typical for measuring instruments:
Measuring range- the range of values of the measured quantity for which the device is designed during its normal operation (with a given measurement accuracy).
Sensitivity threshold- the minimum (threshold) value of the measured value, distinguished by the device.
Sensitivity- connects the value of the measured parameter and the corresponding change in the instrument readings.
Accuracy- the ability of the device to indicate the true value of the measured indicator.
Stability- the ability of the device to maintain a given measurement accuracy for a certain time after calibration.
UNITS OF MEASUREMENT, see UNITS OF WEIGHTS AND MEASURES ... Scientific and technical encyclopedic dictionary
Units- specific values, to the Crimea are assigned numerical values equal to 1. C E. and. they compare and express in them other quantities that are homogeneous with them. By the decision of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (1960), the International System of Units was introduced. SI as a single... ... Dictionary of microbiology
Units- (Mida at Mishkal) Measures of weight, length, area and volume were used in ancient times, mainly for the needs of trade. There are almost no clearly defined unitary measures in the Bible, and it is not easy to establish the relationships between them. At the same time, in... Encyclopedia of Judaism
Units for measuring media capacity and information volume- Units of measurement of information are used to measure various characteristics associated with information. Most often, measuring information concerns measuring the capacity of computer memory (storage devices) and measuring the amount of data transmitted over ... ... Wikipedia
Units for measuring the amount of information- Units of measurement of information are used to measure the volume of information, a value calculated logarithmically. This means that when several objects are considered as one, the number of possible states is multiplied, and the number ... ... Wikipedia
Units of information- serve to measure the volume of information of a value calculated logarithmically. This means that when several objects are considered as one, the number of possible states is multiplied, and the amount of information is added. It doesn’t matter... ... Wikipedia
Pressure units- Pascal (newton per square meter) Bar Millimeter of mercury (torr) Micron of mercury (10−3 torr) Millimeter of water (or water) Atmosphere Physical atmosphere Technical atmosphere Kilogram force per square centimeter, ... ... Wikipedia
UNITS OF MEASUREMENT OF INFORMATION VOLUME- The basis for measuring large amounts of information is the byte. More large units dimensions: kilobyte (1 KB = 1024 bytes), megabyte (1 MB = 1024 KB = 1048576 bytes), gigabyte (1 GB = 1024 MB = 1073741824 bytes). For example, on a sheet... ... Dictionary of business terms
Flow units- Units of flow measurement are a system of measures established in the practice of river flow research, designed to study changes in the water content of rivers over a given period of time. The units of flow measurement include: Instantaneous (second) ... Wikipedia
UNITS OF MEASUREMENT OF PHYSICAL QUANTITIES- quantities that, by definition, are considered equal to unity when measuring other quantities of the same kind. The standard unit of measurement is its physical implementation. Thus, the standard unit of measurement, meter, is a rod 1 m long. In principle, one can imagine... ... Collier's Encyclopedia
Books
- Units of measurement 8-11 years, . Units. 8-11 years old. Compatible with all mathematics programs, development of memory, attention, fine motor skills, motor coordination. Opportunity for self-control and... Buy for 151 rubles
- Units. Workbook for children 6-7 years old, Ignatieva Larisa Viktorovna. Workbook"Units of Measurement" is intended for classes with older children preschool age. The purpose of the manual is to introduce children to units of measurement and terms that they…
All-Russian classifier of units of measurement
All-Russian classifier of units of measurement (OKEY) is part of Unified system classification and coding of technical, economic and social information of the Russian Federation (ESKK).
OKEY is intended for use in solving problems of quantitative assessment of technical, economic and social indicators for the purposes of state accounting and reporting, analysis and forecasting of economic development, ensuring international statistical comparisons, carrying out domestic and foreign trade, state regulation of foreign economic activity and organizing customs control. Objects of classification in OKEY are the units of measurement used in these areas of activity.
Date of placement in the database 06/01/2009
Relevance of the classifier: including changes 7/2000, approved. Gosstandart of the Russian Federation
Showing 460 entries
International units of measurement included in the ESCC
| Code | Symbol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| national | international | national | international | ||
Units of length |
|||||
| 003 | Millimeter | mm | mm | MM | MMT |
| 004 | Centimeter | cm | cm | CM | CMT |
| 005 | Decimeter | dm | dm | DM | DMT |
| 006 | Meter | m | m | M | MTR |
| 008 | Kilometer; thousand meters | km; 10^3 m | km | KM; THOUSAND M | KMT |
| 009 | Megameter; million meters | Mm; 10^6 m | mm | MEGAM; MILLION M | MAM |
| 039 | Inch (25.4 mm) | inch | in | INCH | INH |
| 041 | ft (0.3048 m) | foot | ft | FOOT | FOT |
| 043 | Yard (0.9144 m) | yard | yd | YARD | YRD |
| 047 | Nautical mile (1852 m) | mile | n mile | MILES | NMI |
Area units |
|||||
| 050 | Square millimeter | mm2 | mm2 | MM2 | MMK |
| 051 | Square centimeter | cm2 | cm2 | SM2 | CMK |
| 053 | Square decimeter | dm2 | dm2 | DM2 | DMK |
| 055 | Square meter | m2 | m2 | M2 | MTK |
| 058 | thousand square meters | 10^3 m^2 | yeah | THOUSAND M2 | DAA |
| 059 | Hectare | ha | ha | GA | HAR |
| 061 | Square kilometer | km2 | km2 | KM2 | KMK |
| 071 | Square inch (645.16 mm2) | inch2 | in2 | INCH2 | INK |
| 073 | Square foot (0.092903 m2) | ft2 | ft2 | FOOT2 | FTK |
| 075 | Square yard (0.8361274 m2) | yard2 | yd2 | YARD2 | YDK |
| 109 | Ar (100 m2) | A | a | AR | ARE |
Volume units |
|||||
| 110 | Cubic millimeter | mm3 | mm3 | MM3 | MMQ |
| 111 | Cubic centimeter; milliliter | cm3; ml | cm3; ml | SM3; ML | CMQ; MLT |
| 112 | Liter; cubic decimeter | l; dm3 | I; L; dm^3 | L; DM3 | LTR; DMQ |
| 113 | Cubic meter | m3 | m3 | M3 | MTQ |
| 118 | Deciliter | dl | dl | DL | DLT |
| 122 | Hl | ch | hl | GL | HLT |
| 126 | Megaliter | Ml | Ml | MEGAL | MAL |
| 131 | Cubic inch (16387.1 mm3) | inch3 | in3 | INCH3 | INQ |
| 132 | Cubic foot (0.02831685 m3) | ft3 | ft3 | FOOT3 | FTQ |
| 133 | Cubic yard (0.764555 m3) | yard3 | yd3 | YARD3 | YDQ |
| 159 | Million cubic meters | 10^6 m3 | 10^6 m3 | MLN M3 | HMQ |
Units of mass |
|||||
| 160 | Hectogram | yy | hg | GG | H.G.M. |
| 161 | Milligram | mg | mg | MG | M.G.M. |
| 162 | Metric carat | car | MS | KAR | CTM |
| 163 | Gram | G | g | G | GRM |
| 166 | Kilogram | kg | kg | KG | KGM |
| 168 | Ton; metric ton (1000 kg) | T | t | T | TNE |
| 170 | Kiloton | 10^3 t | kt | CT | KTN |
| 173 | Centigram | sg | cg | SG | CGM |
| 181 | Gross registered ton (2.8316 m3) | BRT | - | BRUTT. REGISTER T | GRT |
| 185 | Load capacity in metric tons | t grp | - | T LOAD UNDER | CCT |
| 206 | Centner (metric) (100 kg); hectokilogram; quintal1 (metric); deciton | ts | q; 10^2 kg | C | DTN |
Technical units |
|||||
| 212 | Watt | W | W | VT | WTT |
| 214 | Kilowatt | kW | kW | KVT | KWT |
| 215 | Megawatt; thousand kilowatts | MW; 10^3 kW | M.W. | MEGAVT; THOUSAND KW | MAW |
| 222 | Volt | IN | V | IN | VLT |
| 223 | Kilovolt | kV | kV | HF | KVT |
| 227 | Kilovolt-ampere | kVA | kV.A | KV.A | KVA |
| 228 | Megavolt-ampere (thousand kilovolt-ampere) | M.V.A | M.V.A | MEGAV.A | MVA |
| 230 | Kilovar | kvar | kVAR | KVAR | KVR |
| 243 | Watt hour | Wh | W.h | VT.H | WHR |
| 245 | Kilowatt hour | kWh | kW.h | KW.H | K.W.H. |
| 246 | Megawatt hour; 1000 kilowatt-hours | MWh; 10^3 kWh | MW.h | MEGAWH; THOUSAND KW.H | MWH |
| 247 | Gigawatt-hour (million kilowatt-hours) | GWh | GW.h | GIGAVT.H | G.W.H. |
| 260 | Ampere | A | A | A | AMP |
| 263 | Ampere hour (3.6 kC) | A.h | A.h | A.Ch | AMH |
| 264 | Thousand amp hours | 10^3 Ah | 10^3 A.h | THOUSAND A.H | TAH |
| 270 | Pendant | Cl | C | KL | COU |
| 271 | Joule | J | J | J | JOU |
| 273 | Kilojoule | kJ | kJ | KJ | K.J.O. |
| 274 | Ohm | Ohm | <омега> | OM | O.H.M. |
| 280 | Degree Celsius | hail C | hail C | CITY OF CELUS | CEL |
| 281 | Fahrenheit | hail F | hail F | CITY OF FARENG | FAN |
| 282 | Candela | cd | CD | KD | C.D.L. |
| 283 | Lux | OK | lx | OK | LUX |
| 284 | Lumen | lm | lm | LM | LUM |
| 288 | Kelvin | K | K | TO | KEL |
| 289 | Newton | N | N | N | NEW |
| 290 | Hertz | Hz | Hz | GC | HTZ |
| 291 | KHz | kHz | kHz | KGC | KHZ |
| 292 | Megahertz | MHz | MHz | MEGAHz | MHZ |
| 294 | Pascal | Pa | Pa | PA | PAL |
| 296 | Siemens | Cm | S | SI | SIE |
| 297 | Kilopascal | kPa | kPa | KPA | KPA |
| 298 | Megapascal | MPa | MPa | MEGAPA | MPA |
| 300 | Physical atmosphere (101325 Pa) | atm | atm | ATM | ATM |
| 301 | Technical atmosphere (98066.5 Pa) | at | at | ATT | A.T.T. |
| 302 | Gigabecquerel | GBk | GBq | GIGABK | GBQ |
| 304 | Millicurie | mCi | mCi | MKI | MCU |
| 305 | Curie | Ki | Ci | CI | CUR |
| 306 | Gram of fissile isotopes | g D/I | g fissile isotopes | G FISSIONING ISOTOPES | GFI |
| 308 | Millibar | mb | mbar | MBAR | MBR |
| 309 | Bar | bar | bar | BAR | BAR |
| 310 | Hectobar | GB | hbar | GBAR | H.B.A. |
| 312 | Kilobar | kb | kbar | KBAR | K.B.A. |
| 314 | Farad | F | F | F | FAR |
| 316 | Kilogram per cubic meter | kg/m3 | kg/m3 | KG/M3 | KMQ |
| 323 | Becquerel | Bk | Bq | BC | BQL |
| 324 | Weber | Wb | Wb | WB | WEB |
| 327 | Knot (mph) | bonds | kn | UZ | KNT |
| 328 | Meter per second | m/s | m/s | M/S | MTS |
| 330 | Revolutions per second | r/s | r/s | OB/S | R.P.S. |
| 331 | Revolutions per minute | rpm | r/min | RPM | RPM |
| 333 | Kilometer per hour | km/h | km/h | KM/H | KMH |
| 335 | Meter per second squared | m/s2 | m/s2 | M/S2 | MSK |
| 349 | Pendant per kilogram | C/kg | C/kg | CL/KG | C.K.G. |
Time units |
|||||
| 354 | Second | With | s | WITH | SEC |
| 355 | Minute | min | min | MIN | MIN |
| 356 | Hour | h | h | H | HUR |
| 359 | Day | days; days | d | SUT; DN | DAY |
| 360 | A week | weeks | - | NED | WEE |
| 361 | Decade | Dec | - | DEC | DAD |
| 362 | Month | months | - | MES | MON |
| 364 | Quarter | quart | - | QUART | QAN |
| 365 | Half year | six months | - | HALF A YEAR | SAN |
| 366 | Year | G; years | a | YEAR; YEARS | ANN |
| 368 | Decade | deslet | - | DESLET | DEC |
Economic units |
|||||
| 499 | kilogram per second | kg/s | - | KG/S | KGS |
| 533 | Ton of steam per hour | t steam/h | - | T STEAM/H | TSH |
| 596 | Cubic meter per second | m3/s | m3/s | M3/S | MQS |
| 598 | Cubic meter per hour | m3/h | m3/h | M3/H | MQH |
| 599 | Thousand cubic meters per day | 10^3 m3/day | - | THOUSAND M3/DAT | TQD |
| 616 | Spool | bean | - | BEAN | NBB |
| 625 | Sheet | l. | - | SHEET | LEF |
| 626 | One hundred sheets | 100 l. | - | 100 SHEET | CLF |
| 630 | Thousand standard conditional bricks | thousand std. conventional brick | - | THOUSAND STANDARD USL KIRP | M.B.E. |
| 641 | Dozen (12 pcs.) | dozen | Doz; 12 | DOZEN | DZN |
| 657 | Product | ed. | - | ISD | NAR |
| 683 | One hundred boxes | 100 boxes | Hbx | 100 BOX | HBX |
| 704 | Kit | kit | - | KIT | SET |
| 715 | Pair (2 pieces) | steam | pr; 2 | STEAM | NPR |
| 730 | Two tens | 20 | 20 | 2 DES | SCO |
| 732 | Ten pairs | 10 pairs | - | DES PAR | TPR |
| 733 | A dozen couples | a dozen pairs | - | A DOZEN PAIRS | DPR |
| 734 | Package | message | - | MESSAGE | NPL |
| 735 | Part | Part | - | PART | NPT |
| 736 | Roll | rul | - | RUL | NPL |
| 737 | A dozen rolls | a dozen rolls | - | A DOZEN RULS | DRL |
| 740 | A dozen pieces | a dozen pieces | - | A DOZEN PCS | DPC |
| 745 | Element | ale | C.I. | ELEM | NCL |
| 778 | Package | pack | - | UPAK | NMP |
| 780 | A dozen packs | dozen pack | - | A DOZEN PACK | DZP |
| 781 | One hundred packs | 100 pack | - | 100 UPAK | CNP |
| 796 | Thing | PC | pc; 1 | PC | PCE; NMB |
| 797 | One hundred pieces | 100 pieces | 100 | 100 PIECES | CEN |
| 798 | A thousand pieces | thousand pieces; 1000 pcs | 1000 | THOUSAND PCS | MIL |
| 799 | A million pieces | 10^6 pcs | 10^6 | MILLION PCS | MIO |
| 800 | Billion pieces | 10^9 pcs | 10^9 | BILLION PCS | MLD |
| 801 | Billion pieces (Europe); trillion pieces | 10^12 pcs | 10^12 | BILL ST (EUR); TRILL PIECE | BIL |
| 802 | Quintillion pieces (Europe) | 10^18 pcs | 10^18 | QUINT PIECE | TRL |
| 820 | Alcohol strength by weight | crepe. alcohol by weight | % mds | CREPE ALCOHOL BY WEIGHT | A.S.M. |
| 821 | Alcohol strength by volume | crepe. alcohol by volume | %vol | CREPE ALCOHOL BY VOLUME | ASV |
| 831 | Liter of pure (100%) alcohol | l 100% alcohol | - | L PURE ALCOHOL | LPA |
| 833 | Hectoliter of pure (100%) alcohol | GL 100% alcohol | - | GL PURE ALCOHOL | HPA |
| 841 | Kilogram of hydrogen peroxide | kg H2O2 | - | KG HYDROGEN PEROXIDE | - |
| 845 | Kilogram of 90% dry matter | kg 90% dry | - | KG 90 PERCENT DRY THINGS | KSD |
| 847 | Ton of 90% dry matter | t 90% dry | - | T 90 PERCENT DRY THINGS | TSD |
| 852 | Kilogram of potassium oxide | kg K2O | - | KG POTASSIUM OXIDE | KPO |
| 859 | Kilogram of potassium hydroxide | kg KOH | - | KG POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE | KPH |
| 861 | Kilogram of nitrogen | kg N | - | KG NITROGEN | KNI |
| 863 | Kilogram of sodium hydroxide | kg NaOH | - | KG SODIUM HYDROXIDE | KSH |
| 865 | Kilogram of phosphorus pentoxide | kg Р2О5 | - | KG PHOSPHORUS PENTOXIDE | KPP |
| 867 | Kilogram of uranium | kg U | - | KG URAN | KUR |
National units of measurement included in the ESCC
| Code | Unit name | Symbol | Code letter designation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| national | international | national | international | ||
Units of length |
|||||
| 018 | Linear meter | linear m | POG M | ||
| 019 | One thousand linear meters | 10^3 linear m | THOUSAND LOG M | ||
| 020 | Conventional meter | conventional m | USL M | ||
| 048 | Thousand conventional meters | 10^3 arb. m | THOUSAND USL M | ||
| 049 | Kilometer of conventional pipes | km conventional pipes | KM USL PIPES | ||
Area units |
|||||
| 054 | One thousand square decimeters | 10^3 dm2 | THOUSAND DM2 | ||
| 056 | Million square decimeters | 10^6 dm2 | MLN DM2 | ||
| 057 | Million square meters | 10^6 m2 | MLN M2 | ||
| 060 | Thousand hectares | 10^3 ha | THOUSAND hectares | ||
| 062 | Conventional square meter | conventional m2 | USL M2 | ||
| 063 | One thousand conventional square meters | 10^3 arb. m2 | THOUSAND USL M2 | ||
| 064 | Million conventional square meters | 10^6 arb. m2 | MLN USL M2 | ||
| 081 | Square meter of total area | m2 total pl | M2 GEN PL | ||
| 082 | One thousand square meters of total area | 10^3 m2 total. pl | THOUSAND M2 GENERAL PLUS | ||
| 083 | Million square meters of total area | 10^6 m2 total. pl | MLN M2. GEN PL | ||
| 084 | Square meter of living space | m2 lived. pl | M2 ZHIL PL | ||
| 085 | One thousand square meters of living space | 10^3 m2 veins. pl | THOUSAND M2 LIVED PL | ||
| 086 | Million square meters of living space | 10^6 m2 veins. pl | MILLION M2 LIVED PL | ||
| 087 | Square meter of educational and laboratory buildings | m2 uch. lab. built | M2 UCH.LAB BUILDING | ||
| 088 | One thousand square meters of educational and laboratory buildings | 10^3 m2 uch. lab. built | THOUSAND M2 ACCOUNT. LAB BUILDING | ||
| 089 | One million square meters in two-millimeter terms | 10^6 m2 2 mm calc. | MLN M2 2MM ISCH | ||
Volume units |
|||||
| 114 | Thousand cubic meters | 10^3 m3 | THOUSAND M3 | ||
| 115 | Billion cubic meters | 10^9 m3 | BILLION M3 | ||
| 116 | Deciliter | dkl | DCL | ||
| 119 | One thousand deciliters | 10^3 dcl | THOUSAND DCL | ||
| 120 | Million deciliters | 10^6 dcl | MLN DCL | ||
| 121 | Dense cubic meter | dense m3 | DENSITY M3 | ||
| 123 | Conventional cubic meter | conventional m3 | USL M3 | ||
| 124 | One thousand conventional cubic meters | 10^3 arb. m3 | THOUSAND USL M3 | ||
| 125 | Million cubic meters of gas processing | 10^6 m3 recyclable gas | MILLION M3 GAS PROCESSED | ||
| 127 | One thousand dense cubic meters | 10^3 density m3 | THOUSAND DENSITY M3 | ||
| 128 | One thousand half liters | 10^3 floors l | THOUSAND FLOOR L | ||
| 129 | A million half liters | 10^6 floors l | MILLION FLOOR L | ||
| 130 | One thousand liters; 1000 liters | 10^3 l; 1000 l | YOU SL | ||
Units of mass |
|||||
| 165 | Thousand carats metric | 10^3 ct | THOUSAND CAR | ||
| 167 | Million carats metric | 10^6 ct | MILLION CAR | ||
| 169 | thousand tons | 10^3 t | THOUSAND T | ||
| 171 | Million tons | 10^6 t | MILLION T | ||
| 172 | Ton of standard fuel | t conv. fuel | T USL TOPL | ||
| 175 | One thousand tons of standard fuel | 10^3 t conv. fuel | THOUSAND T USL FUEL | ||
| 176 | Million tons of standard fuel | 10^6 t conv. fuel | MLN T USL FUEL | ||
| 177 | Thousand tons of simultaneous storage | 10^3 t one-time storage | THOUSAND T EDINOVR STORAGE | ||
| 178 | Thousand tons of processing | 10^3 t processed | THOUSAND T PROCESSED | ||
| 179 | Conventional ton | conventional T | USL T | ||
| 207 | One thousand centners | 10^3 c | THOUSAND C | ||
Technical units |
|||||
| 226 | Volt-amps | V.A | V.A | ||
| 231 | Meter per hour | m/h | M/H | ||
| 232 | Kilocalorie | kcal | KKAL | ||
| 233 | Gigacalorie | Gcal | GIGAKAL | ||
| 234 | One thousand gigacalories | 10^3 Gcal | THOUSAND GIGACAL | ||
| 235 | One million gigacalories | 10^6 Gcal | MILLION GIGAKAL | ||
| 236 | Calorie per hour | cal/h | CAL/H | ||
| 237 | Kilocalorie per hour | kcal/h | KKAL/H | ||
| 238 | Gigacalorie per hour | Gcal/h | GIGAKAL/H | ||
| 239 | One thousand gigacalories per hour | 10^3 Gcal/h | THOUSAND GIGACAL/H | ||
| 241 | Million amp hours | 10^6 Ah | MLN A.H. | ||
| 242 | Million kilovolt-amperes | 10^6 kVA | MLN sq.A | ||
| 248 | Kilovolt-ampere reactive | kV.A R | KV.A R | ||
| 249 | Billion kilowatt-hours | 10^9 kWh | BILLION KW.H | ||
| 250 | Thousand kilovolt-amperes reactive | 10^3 kVA R | THOUSAND SQ.A R | ||
| 251 | Horsepower | l. With | PM | ||
| 252 | thousand horsepower | 10^3 l. With | THOUSAND PM | ||
| 253 | Million horsepower | 10^6 l. With | MLN drugs | ||
| 254 | Bit | bit | BIT | ||
| 255 | Byte | bye | BYTE | ||
| 256 | Kilobyte | kbyte | KBYTE | ||
| 257 | Megabyte | MB | MBYTE | ||
| 258 | Baud | baud | BAUD | ||
| 287 | Henry | Gn | GN | ||
| 313 | Tesla | Tl | TL | ||
| 317 | Kilogram per square centimeter | kg/cm^2 | KG/SM2 | ||
| 337 | Millimeter of water column | mm water st | MM VOD ST | ||
| 338 | Millimeter of mercury | mmHg st | MMHG | ||
| 339 | Centimeter of water column | cm water st | SM VOD ST | ||
Time units |
|||||
| 352 | Microsecond | mks | ISS | ||
| 353 | Millisecond | MLS | MLS | ||
Economic units |
|||||
| 383 | Ruble | rub | RUB | ||
| 384 | Thousand rubles | 10^3 RUR | THOUSAND ROUBLES | ||
| 385 | One million rubles | 10^6 RUR | MILLION RUB | ||
| 386 | Billion rubles | 10^9 RUR | BILLION RUB | ||
| 387 | A trillion rubles | 10^12 rub. | TRILL RUB | ||
| 388 | Quadrillion rubles | 10^15 rub. | SQUARE RUB | ||
| 414 | Passenger-kilometer | pass.km | PASS.KM | ||
| 421 | Passenger seat (passenger seats) | pass. places | PASS SEATS | ||
| 423 | Thousand passenger kilometers | 10^3 passenger km | THOUSAND PASS.KM | ||
| 424 | Million passenger kilometers | 10^6 pass. km | MILLION PASS.KM | ||
| 427 | Passenger traffic | pass.flow | PASS.FLOW | ||
| 449 | Ton-kilometer | t.km | T.KM | ||
| 450 | Thousand ton-kilometers | 10^3 t.km | THOUSAND T.KM | ||
| 451 | Million ton-kilometers | 10^6 t. km | MILLION T.KM | ||
| 479 | Thousand sets | 10^3 set | THOUSAND SET | ||
| 510 | Gram per kilowatt hour | g/kWh | G/KW.H | ||
| 511 | Kilogram per gigacalorie | kg/Gcal | KG/GIGAKAL | ||
| 512 | Tonnage number | sono.no. | T.NOM | ||
| 513 | Autoton | auto t | AUTO T | ||
| 514 | Ton of thrust | t.thrust | T traction | ||
| 515 | Deadweight ton | dwt.t | DEADWEIGHT.T | ||
| 516 | Tonno-tanid | t. tanid | T.TANID | ||
| 521 | Person per square meter | person/m2 | PERSON/M2 | ||
| 522 | Persons per square kilometer | person/km2 | PERSON/KM2 | ||
| 534 | ton per hour | t/h | T/H | ||
| 535 | Ton per day | t/day | T/SUT | ||
| 536 | Ton per shift | t/shift | T/SHIFT | ||
| 537 | Thousand tons per season | 10^3 t/s | THOUSAND T/SEZ | ||
| 538 | Thousand tons per year | 10^3 t/year | THOUSAND T/YEAR | ||
| 539 | Man-hour | person/hour | PERSON.H | ||
| 540 | Man-day | person days | PEOPLE DAYS | ||
| 541 | Thousand man-days | 10^3 person days | THOUSAND PEOPLE DAYS | ||
| 542 | Thousand man-hours | 10^3 person/h | THOUSAND PERSONS | ||
| 543 | One thousand standard cans per shift | 10^3 arb. bank/ change | THOUSAND USL BANK/CHANGE | ||
| 544 | Million units per year | 10^6 units/year | MILLION UNITS/YEAR | ||
| 545 | Visit during shift | visits/shifts | VISIT/SHIFT | ||
| 546 | Thousands of visits per shift | 10^3 visits/shift | THOUSAND VISITS/SHIFT | ||
| 547 | Couple per shift | pairs/shifts | PAIR/SHIFT | ||
| 548 | Thousand pairs per shift | 10^3 pairs/shift | THOUSAND PAIRS/SHIFT | ||
| 550 | Million tons per year | 10^6 t/year | MILLION T/YEAR | ||
| 552 | Ton of processing per day | t processed/day | T PROCESSED/DAT | ||
| 553 | Thousand tons of processing per day | 10^3 t processed/day | THOUSAND T PROCESSED/Day | ||
| 554 | Centner of processing per day | c/day | C PROCESS/DAT | ||
| 555 | One thousand centners of processing per day | 10^3 c/day | THOUSAND CENTERS PROCESSED/Day | ||
| 556 | Thousand heads per year | 10^3 goal/year | THOUSAND GOALS/YEAR | ||
| 557 | Million heads per year | 10^6 goal/year | MILLION GOAL/YEAR | ||
| 558 | Thousand bird places | 10^3 bird places | THOUSAND BIRD PLACES | ||
| 559 | Thousand laying hens | 10^3 chickens nonsushi | THOUSAND CHICKS. NESUSH | ||
| 560 | Minimum wage | min. salary boards | MIN SALARY | ||
| 561 | Thousand tons of steam per hour | 10^3 t steam/h | THOUSAND T STEAM/H | ||
| 562 | A thousand spindles | 10^3 strands spun | A THOUSAND STRAINS BELIEVE | ||
| 563 | A thousand spinning places | 10^3 rows | THOUSAND ROW OF SEATS | ||
| 639 | Dose | doses | DOZ | ||
| 640 | A thousand doses | 10^3 doses | THOUSAND DOSES | ||
| 642 | Unit | units | ED | ||
| 643 | Thousand units | 10^3 units | THOUSAND UNITS | ||
| 644 | Million units | 10^6 units | MILLION UNITS | ||
| 661 | Channel | channel | CHANNEL | ||
| 673 | Thousand sets | 10^3 sets | THOUSAND SET | ||
| 698 | Place | places | PLACE | ||
| 699 | A thousand places | 10^3 seats | THOUSAND PLACES | ||
| 709 | A thousand numbers | 10^3 nom | THOUSAND NUM | ||
| 724 | A thousand hectares of portions | 10^3 ha portions | THOUSAND hectares PORTS | ||
| 729 | Thousand packs | 10^3 pack | THOUSAND PACKS | ||
| 744 | Percent | % | PERCENT | ||
| 746 | ppm (0.1 percent) | ppm | PROMILLE | ||
| 751 | A thousand rolls | 10^3 roll | THOUSAND RUL | ||
| 761 | A thousand stans | 10^3 stan | THOUSAND STAN | ||
| 762 | Station | stanza | STANCE | ||
| 775 | A thousand tubes | 10^3 tube | THOUSAND TUBE | ||
| 776 | A thousand conditional tubes | 10^3 conventional tubes | THOUSAND USL TUBE | ||
| 779 | Million packs | 10^6 pack | MLN UPAK | ||
| 782 | Thousand packs | 10^3 pack | THOUSAND PACK | ||
| 792 | Human | people | PERSON | ||
| 793 | A thousand people | 10^3 people | THOUSAND PEOPLE | ||
| 794 | A million people | 10^6 people | MILLION PEOPLE | ||
| 808 | A million copies | 10^6 copies | MILLION EKZ | ||
| 810 | Cell | yach | YACH | ||
| 812 | Box | box | BOX | ||
| 836 | Head | Goal | GOAL | ||
| 837 | A thousand pairs | 10^3 pairs | THOUSAND PAIRS | ||
| 838 | A million couples | 10^6 pairs | MILLION PAIRS | ||
| 839 | Set | set | COMPLETE | ||
| 840 | Section | section | SECC | ||
| 868 | Bottle | bottle | BUT | ||
| 869 | Thousand bottles | 10^3 bottle | THOUSAND BUT | ||
| 870 | Ampoule | ampoules | AMPOULES | ||
| 871 | Thousand ampoules | 10^3 ampoules | THOUSAND AMPOULES | ||
| 872 | Bottle | flak | FLAC | ||
| 873 | A thousand bottles | 10^3 bottle | THOUSAND FLAC | ||
| 874 | Thousand tubes | 10^3 tubes | THOUSAND TUBES | ||
| 875 | A thousand boxes | 10^3 cor | THOUSAND COR | ||
| 876 | Conventional unit | conventional units | USL ED | ||
| 877 | Thousand conventional units | 10^3 arb. units | THOUSAND USL UNITS | ||
| 878 | Million conventional units | 10^6 arb. units | MILLION USL UNITS | ||
| 879 | Conditional thing | conventional PC | USL SHT | ||
| 880 | A thousand conventional pieces | 10^3 arb. PC | THOUSAND USL PCS | ||
| 881 | Conditional bank | conventional bank | USL BANK | ||
| 882 | A thousand conditional cans | 10^3 arb. bank | TUS USL BANK | ||
| 883 | A million conditional cans | 10^6 arb. bank | MLN USL BANK | ||
| 884 | Conditional piece | conventional bite | USL KUS | ||
| 885 | A thousand conventional pieces | 10^3 arb. bite | THOUSAND USL KUS | ||
| 886 | A million conventional pieces | 10^6 arb. bite | MLN USL KUS | ||
| 887 | Conditional box | conventional box | USL BOX | ||
| 888 | A thousand conditional boxes | 10^3 arb. box | THOUSAND US BOXES | ||
| 889 | Conditional coil | conventional cat | USL CAT | ||
| 890 | Thousand conditional coils | 10^3 arb. cat | THOUSAND USL CAT | ||
| 891 | Conditional tile | conventional slabs | USL PLATES | ||
| 892 | A thousand conditional tiles | 10^3 arb. slabs | THOUSAND USL PLATES | ||
| 893 | Conditional brick | conventional brick | USL KIRP | ||
| 894 | A thousand conditional bricks | 10^3 arb. brick | THOUSAND USL KIRP | ||
| 895 | A million conditional bricks | 10^6 arb. brick | MLN USL KIRP | ||
| 896 | Family | families | FAMILIES | ||
| 897 | A thousand families | 10^3 families | THOUSAND FAMILIES | ||
| 898 | A million families | 10^6 families | MILLION FAMILIES | ||
| 899 | The household | housekeeping | HOUSEHOLD | ||
| 900 | Thousand households | 10^3 household | THOUSAND HOUSEHOLDS | ||
| 901 | Million households | 10^6 household | MILLION HOUSEHOLDS | ||
| 902 | Student place | scientist places | PLACE STUDYED | ||
| 903 | Thousand student places | 10^3 sc. places | THOUSAND PLACES STUDYED | ||
| 904 | Workplace | slave. places | SLAVE PLACES | ||
| 905 | A thousand jobs | 10^3 work. places | THOUSAND WORK PLACES | ||
| 906 | Seat | Posad places | POSAD SEATS | ||
| 907 | Thousands of seats | 10^3 seating places | THOUSAND SEATS | ||
| 908 | Number | nom | NOM | ||
| 909 | Apartment | quart | QUART | ||
| 910 | A thousand apartments | 10^3 quarts | THOUSAND QUARTERS | ||
| 911 | Bed | beds | BOOK | ||
| 912 | A thousand beds | 10^3 beds | THOUSAND BEDS | ||
| 913 | Volume of the book fund | book volume fund | TOM BOOK FOUNDATION | ||
| 914 | Thousand volumes of the book fund | 10^3 volume. book fund | THOUSAND VOLUME BOOK FUND | ||
| 915 | Conditional repair | conventional rem | USL REM | ||
| 916 | Conditional repairs per year | conventional rem/year | USL REM/YEAR | ||
| 917 | Change | shifts | SHIFT | ||
| 918 | Author's sheet | l. auto | SHEET AVT | ||
| 920 | Printed sheet | l. oven | SHEET OVEN | ||
| 921 | Recording and publishing sheet | l. academic ed. | STUDY SHEET | ||
| 922 | Sign | sign | SIGN | ||
| 923 | Word | word | WORD | ||
| 924 | Symbol | symbol | SYMBOL | ||
| 925 | Conventional pipe | conventional pipes | USL PIPES | ||
| 930 | Thousand plates | 10^3 layer | THOUSAND PLAST | ||
| 937 | A million doses | 10^6 doses | MILLION DOSES | ||
| 949 | A million sheets of prints | 10^6 sheet.print | MILLION SHEET.PRINT | ||
| 950 | Car (car)-day | vag (mash).dn | VAG (MASH).DN | ||
| 951 | A thousand car-(machine)-hours | 10^3 vag (mash).h | THOUSAND VAG (MASH).H | ||
| 952 | One thousand car-(vehicle)-kilometers | 10^3 vag (mach).km | THOUSAND VAG (MASH).KM | ||
| 953 | A thousand place-kilometers | 10 ^3 places.km | THOUSAND PLACE KM | ||
| 954 | Car-day | vag.day | VAG.SUT | ||
| 955 | One thousand train hours | 10^3 train.h | THOUSAND TRAIN.H | ||
| 956 | A thousand train kilometers | 10^3 train.km | THOUSAND TRAIN KM | ||
| 957 | Thousand ton miles | 10^3 t.miles | THOUSAND T.MILES | ||
| 958 | Thousand passenger miles | 10^3 passenger miles | THOUSAND PASSENGER MILES | ||
| 959 | Car-day | car days | CAR.DN | ||
| 960 | Thousand vehicle-ton-days | 10^3 cart.d. | THOUSAND VEHICLES.T.D.N. | ||
| 961 | Thousand car-hours | 10^3 car.h | THOUSAND VEHICLES.H | ||
| 962 | A thousand car-seat-days | 10^3 car spaces days | THOUSAND CAR SEATS DN | ||
| 963 | Given hour | drive.h | DRIVE.H | ||
| 964 | Aircraft-kilometer | plane.km | AIRPLANE.KM | ||
| 965 | A thousand kilometers | 10^3 km | THOUSAND KM | ||
| 966 | Thousand tonnage flights | 10^3 tonnage. flight | THOUSAND TONNAGE. FLIGHT | ||
| 967 | Million ton miles | 10^6 t. miles | MILLION T. MILES | ||
| 968 | Million passenger miles | 10^6 pass. miles | MILLION PASS. MILES | ||
| 969 | Million tonnage miles | 10^6 tonnage. miles | MILLION TONNAGE. MILES | ||
| 970 | Million passenger-seat-miles | 10^6 pass. places miles | MILLION PASS. LOCATION MILES | ||
| 971 | Feed day | feed. days | FEED. DN | ||
| 972 | Centner of feed units | c feed units | C FEED UNIT | ||
| 973 | Thousand car-kilometers | 10^3 cars km | THOUSAND CARS KM | ||
| 974 | Thousand tonnage-day | 10^3 tonnage. days | THOUSAND TONNAGE. SUT | ||
| 975 | Sugo-day | sugo. days | SUGO. SUT | ||
| 976 | Units per 20-foot equivalent unit (TEU) | pieces in 20 foot equivalent | PCS IN 20 FEET EQUIV | ||
| 977 | Channel-kilometer | channel. km | CHANNEL. KM | ||
| 978 | Channel ends | channel. conc. | CHANNEL. END | ||
| 979 | One thousand copies | 10^3 copies | THOUSAND EXECUTES | ||
| 980 | One thousand dollars | 10^3 dollar | THOUSAND DOLLAR | ||
| 981 | Thousand tons of feed units | 10^3 food units | THOUSAND TON OF FEED UNITS | ||
| 982 | Million tons of feed units | 10^6 food units | MILLION TON OF FEED UNITS | ||
| 983 | Sudo-day | court.day | COURT.SUT | ||
International units of measurement not included in the ESCC
| Code | Unit name | Symbol | Code letter designation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| national | international | national | international | ||
Units of length |
|||||
| 017 | Hectometer | hm | HMT | ||
| 045 | Mile (statute) (1609.344 m) | mile | SMI | ||
Area units |
|||||
| 077 | Acre (4840 square yards) | acre | ACR | ||
| 079 | Square mile | mile2 | MIK | ||
Volume units |
|||||
| 135 | Fluid ounce SC (28.413 cm3) | fl oz (UK) | OZI | ||
| 136 | Jill SK (0.142065 dm3) | Gill (UK) | GII | ||
| 137 | Pint SK (0.568262 dm3) | pt (UK) | PTI | ||
| 138 | Quart SK (1.136523 dm3) | qt (UK) | QTI | ||
| 139 | Gallon SC (4.546092 dm3) | gal (UK) | GLI | ||
| 140 | Bushel SK (36.36874 dm3) | bu (UK) | BUI | ||
| 141 | US fluid ounce (29.5735 cm3) | fl oz (US) | OZA | ||
| 142 | Jill US (11.8294 cm3) | Gill (US) | GIA | ||
| 143 | US liquid pint (0.473176 dm3) | liq pt (US) | PTL | ||
| 144 | US liquid quart (0.946353 dm3) | liq qt (US) | QTL | ||
| 145 | US liquid gallon (3.78541 dm3) | gal (US) | GLL | ||
| 146 | Barrel (oil) USA (158.987 dm3) | barrel (US) | BLL | ||
| 147 | Dry US pint (0.55061 dm3) | dry pt (US) | PTD | ||
| 148 | US dry quart (1.101221 dm3) | dry qt (US) | QTD | ||
| 149 | Dry US gallon (4.404884 dm3) | dry gal (US) | GLD | ||
| 150 | US bushel (35.2391 dm3) | bu (US) | BUA | ||
| 151 | US dry barrel (115.627 dm3) | bbl (US) | BLD | ||
| 152 | Standard | - | WSD | ||
| 153 | Cord (3.63 m3) | - | WCD | ||
| 154 | Thousands of board feet (2.36 m3) | - | MBF | ||
Units of mass |
|||||
| 182 | Net register ton | - | NTT | ||
| 183 | Measured (freight) ton | - | SHT | ||
| 184 | Displacement | - | DPT | ||
| 186 | UK pound, US (0.45359237 kg) | lb | LBR | ||
| 187 | Ounce UK, US (28.349523 g) | oz | ONZ | ||
| 188 | Drachma SK (1.771745 g) | dr | DRI | ||
| 189 | Gran SK, USA (64.798910 mg) | gn | GRN | ||
| 190 | Stone SK (6.350293 kg) | st | STI | ||
| 191 | Kvarter SK (12.700586 kg) | qtr | QTR | ||
| 192 | Central SK (45.359237 kg) | - | CNT | ||
| 193 | US cwt (45.3592 kg) | cwt | C.W.A. | ||
| 194 | Long quintal SK (50.802345 kg) | cwt (UK) | CWI | ||
| 195 | Short ton UK, USA (0.90718474 t) | sht | STN | ||
| 196 | Long ton UK, USA (1.0160469 t) | lt | LTN | ||
| 197 | Scrupul SK, USA (1.295982 g) | scr | SCR | ||
| 198 | Pennyweight UK, USA (1.555174 g) | dwt | DWT | ||
| 199 | Drachma SK (3.887935 g) | drm | DRM | ||
| 200 | US drachma (3.887935 g) | - | DRA | ||
| 201 | Ounce UK, US (31.10348 g); troy ounce | apoz | APZ | ||
| 202 | US troy pound (373.242 g) | - | LBT | ||
Technical units |
|||||
| 213 | Effective power (245.7 watts) | B.h.p. | BHP | ||
| 275 | British thermal unit (1.055 kJ) | Btu | BTU | ||
Economic units |
|||||
| 638 | Gross (144 pcs.) | gr; 144 | GRO | ||
| 731 | Big gross (12 gross) | 1728 | GGR | ||
| 738 | Short standard (7200 units) | - | SST | ||
| 835 | Gallon of alcohol of specified strength | - | P.G.L. | ||
| 851 | International unit | - | NIU | ||
| 853 | One hundred international units | - | HIU | ||