Bryophyte department- these are higher spore plants, the species diversity of which reaches 20 thousand. The study of mosses has been going on for many centuries, the scientists involved in their research were called bryologists, they founded a separate botanical branch dedicated to bryophytes - bryology. Briology - the science of mosses, studies the structure, reproduction and development of bryophytes (actually mosses, liverworts, anthocerotes).
General characteristics of mosses
Moss - general characteristics
Bryophytes are one of the oldest plants that inhabit our planet. The remains are found in fossils from the end of the Paleozoic era. The distribution of mosses is associated with a preference for a humid environment and shaded areas, so the majority inhabit the northern part of the Earth. Poorly take root in saline areas and deserts.
Bryophyte classes
Leafy mosses is the most numerous class. Plants are composed of stem, leaves and rhizoids.
Stem can grow vertically or horizontally, divided into bark and main tissue (contains water, starch, chloroplasts for photosynthesis).
Stem cells can produce filamentous processes - rhizoids, necessary for anchoring to the soil and absorbing water. They are often located at the base of the stem, but can cover it along its entire length.
Leaves simple, often attached to the stem at a right angle, in a spiral. Leaf blades are equipped with chloroplasts, in the center there is a vein (serves to carry nutrients).
Deciduous mosses can reproduce by stems, buds, branches, which give rise to the formation of solid carpets of mosses that cover the ground. The class of leafy plants includes sphagnum mosses (they have a variety of stem colors - light green, yellow, red), andreevy and bry mosses.
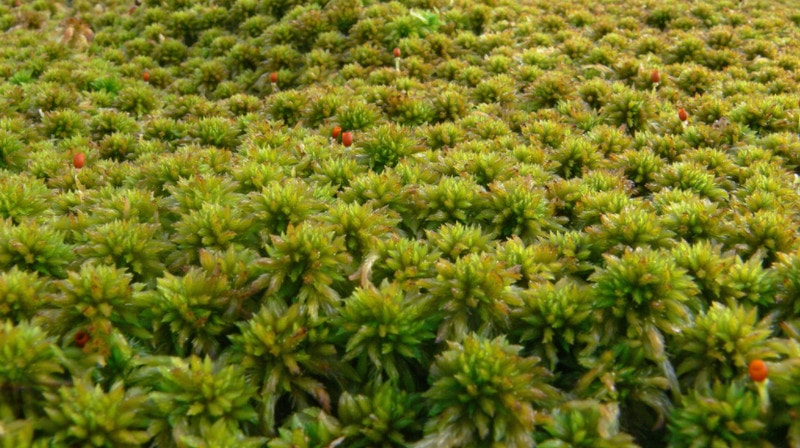

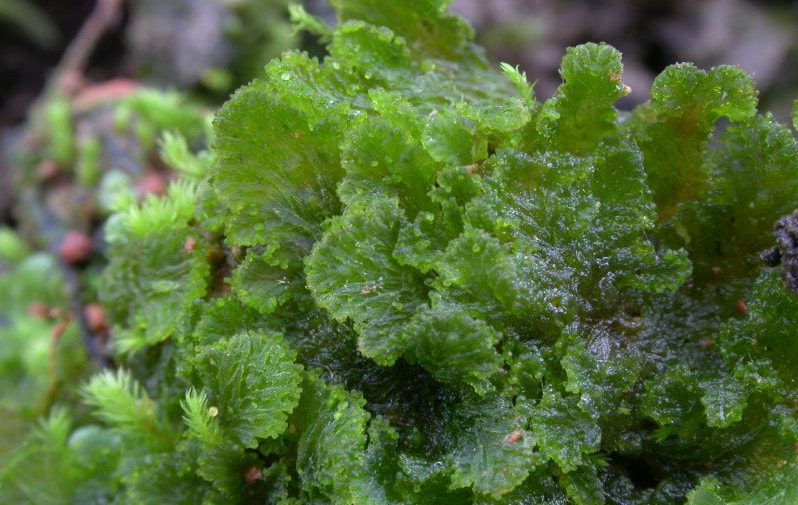
liverworts found on the coasts, swamps, rocky terrain. Distinctive features: leaves do not have a vein, dorsoventral structure, a special mechanism for opening the sporophyte.
The leaves are arranged in rows, have two lobes (the lower lobe is often wrapped and serves as a reservoir for water), rhizoidal processes are unicellular. During the rash of spores, the sporophyte box opens into separate valves, and elaters (spring formations) contribute to the dispersion of cells.
Reproduction can be carried out with the help of buds (vegetatively), which are formed at the upper pole of the leaves. Representatives of the class pella endievistnaya, milia anomalous, moss marchantia, etc.
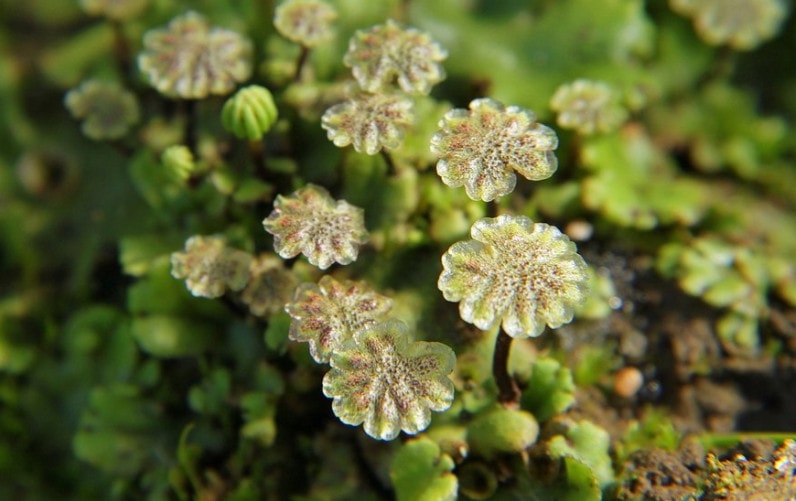

Anthocerotus mosses inhabit the tropical zone. The multinuclear body (thallus) has a rosette shape, consists of the same type of cells. In the upper balls of cells are chromatophores (contain a dark green pigment). The lower part of the thallus gives rise to processes, rhizoids, the body itself forms cavities filled with a viscous fluid that maintains constant moisture.
On the surface of the thallus, under adverse conditions, tubers are formed that are resistant to low humidity; after a period of drought, a new generation is formed. Plants are monoecious, reproductive organs develop in the thickness of the thallus, the sporophyte stage is predominant. Anthocerotes include folioceros, anthoceros, notothilas, etc.

How do mosses reproduce?
There is an alternation of asexual and sexual reproduction in the life cycle of mosses. The asexual period begins with the formation of spores and their germination on moist soil (a pregrowth is formed, a thin thread that gives life to male and female individuals). There are two types of mosses:
monoecious- male and female reproductive organs are on the same plant.
Dioecious- Reproductive organs are located in different representatives of the sex.
After the spore germinates, the moss life cycle enters the sexual phase. The organs of sexual reproduction are antheridia (male) and archegonia (female). Representatives of males are weaker than females, smaller in size, after the formation of antheridia they die off.
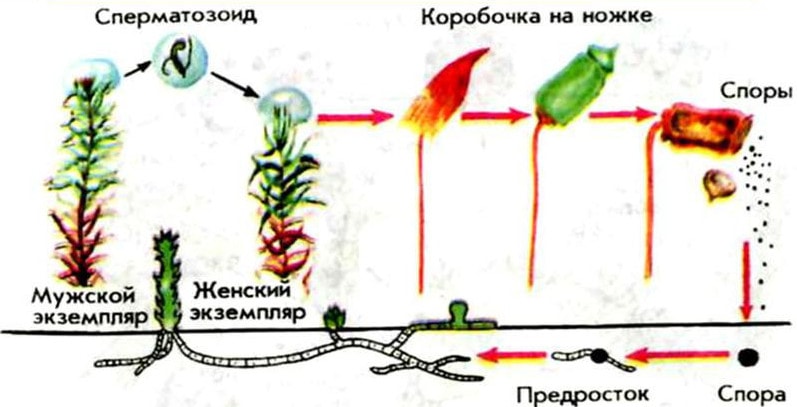
Spermatozoa are formed on male plants, eggs on female plants, after their fusion a zygote is formed (located on the female, it feeds the immature sporophyte), which later develops into a sporangium. After maturation of the sporangium, it opens, spores spill out of it - the asexual reproduction period of mosses begins again.
Reproduction of offspring is possible in a vegetative way, mosses form thalli (green branches), buds, tubers, which take root well on moist soil.
What is the importance of spores in the life of mosses?
Spores are the cells that mosses need to reproduce. Moss plants do not bloom, do not have roots, therefore, in order to continue the genus, they have formed a sporophyte with sporangia (the place where spores ripen).
The sporophyte has a short life cycle; after drying, the spores disperse around, and when they get on moist soil, they quickly take root. Under unfavorable conditions, they can persist for a long time without germinating, resistant to low and high temperatures, and prolonged droughts.
The value of mosses in nature and human life
Mosses are food for many invertebrates.
After dying, they give deposits of peat, which is necessary in the production of plastics, resins, carbolic acid, and is used as fuel or fertilizer.
Moss completely covers the ground in places of growth, which leads to the accumulation of moisture and waterlogging of the territory. Thus, the germination of other vegetation becomes impossible. At the same time, they prevent erosion, soil destruction by surface water and winds. When the mosses die off, they take part in the formation of the soil.
Able to grow in places of fires, persistent and hardy, they inhabit the territory of the tundra (the main vegetation background, since other plants cannot survive in such conditions).
In wartime, sphagnum moss was used as a dressing because of its bactericidal properties and ability to absorb moisture.
With the help of mosses, you can navigate the terrain: they do not like light, therefore they are located on the shady side of stones and trees. Moss points the man to the north.
In construction, it is used as an insulating, insulating material.