1. Mark the forms of higher nervous activity that are common to humans and animals (see § 60).
2. Ivan Petrovich Pavlov attributed all objects and phenomena of the outside world to the first signal system, and speech to the second signal system. He believed that objects and phenomena of the external world can be designated and replaced by a word. Is the converse statement true: each word corresponds to certain phenomena and objects?
Support your answer with facts.
Yes. Each word means something: an object (Vasya, a table, the Moon) or a phenomenon (thunderstorm, snowfall, whisper).
3. Each word is characterized by a generalization. Does the word one generalize?
Yes.
WORK 181
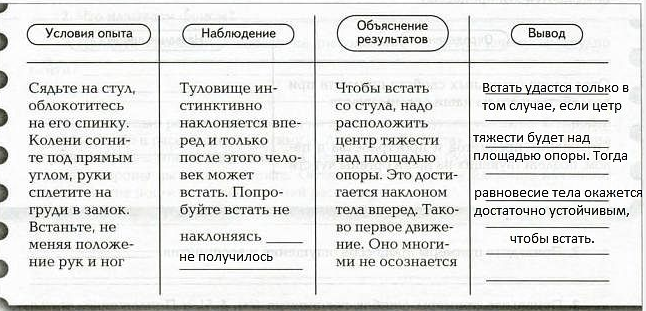
1. Are all our movements conscious? Experiment to find out. Fill the table.
WORK 182
1. Finish the statement.
The human brain has speech centers. However, which language he "speaks" depends on his language environment.
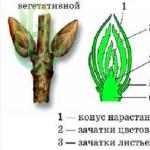
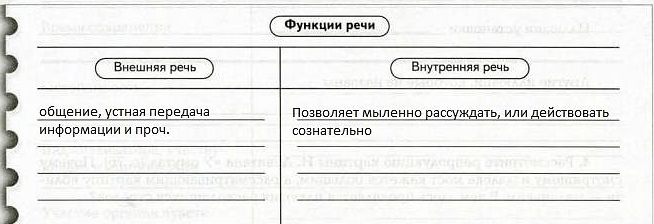
2. It is known that speech performs two functions. Name them.
WORK 183
The study of cognitive processes begins with sensations and perceptions.
1. On the left in the table are definitions of two cognitive processes. What are these processes called?
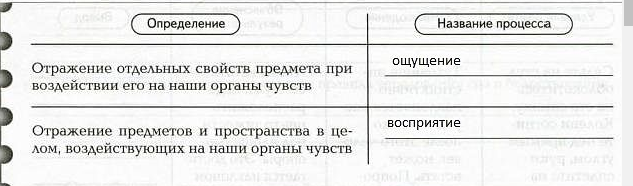
2. Give examples of the processes of sensation and perception.
Sensation: bitter taste, hot kettle; perception: speech, sounds.
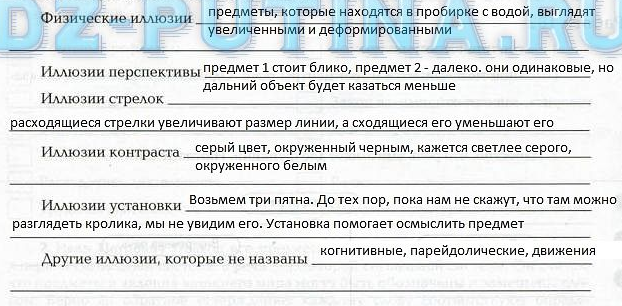
3. Give examples of perceptual errors (see §51 and Appendix, article "Do not believe your eyes - an illusion", p. 266).
4. Consider a reproduction of the painting by I. Levitan "At the pool" (p. 76). Why does the bridge seem large to those looking from a distance, but small to those looking at the picture from a distance? What is the illusion of diverging arrows here?
This is the principle of perspective, which assumes that all parallel lines converge at the horizon, and the size of an object decreases proportionally as it moves away from the observer.
WORK 184
1. What do we call the object of perception?
Thing, phenomenon or process, which is aimed at subject-practical and cognitive activity.
2. What is called the background?
The color or shape that surrounds an object.
3. Find the missing dog in Figure 109 (p. 268). Why is it hard to find?
Because the spots of the dog have merged with the general background.
4. With the help of speech, you can influence the perception of another person. Open your notebook to p. 76 and look at the picture by I. Levitan “At the pool”. Pay attention to the cut logs of the bridge connecting the banks of the river. They will be facing you from which side you look. Explain why this illusion is seen by many after this, as they are told about it.
This is the Illusion of Installation. If you tell a person about an illusion, he will notice it, despite the fact that he did not notice it before.
WORK 185
1. Identify a cognitive process in which, based on speech, you can store past experiences in your mind and reuse them.
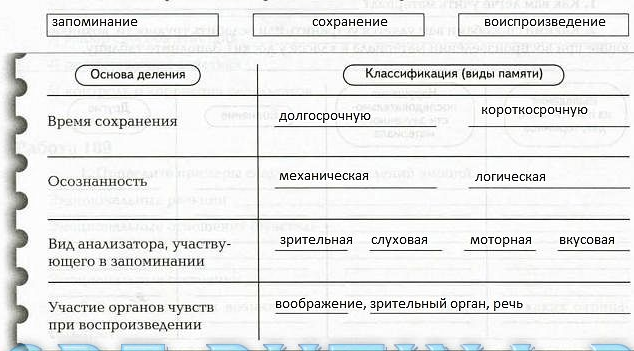
2. Indicate the three main memory processes and list the types of memory in the table.
3. Test your mechanical and logical memory. Try to memorize 10 words from the first row in 1 minute, and then 10 words from the second row.

WORK 186
1. How do you find it easier to learn the material?
Visually.
2. In what ways do you manage to eliminate or reduce the difficulties that arise when reproducing material in the classroom at the blackboard? Fill the table.
WORK 187
Analyze the plot and write where the researcher relied on perception, and where - on the processes of thinking?