According to the latest scientific data, the ancestors of modern fish - jawless animals that resemble them in appearance - lived already in the early Cambrian, about 530 million years ago. It is conceivable that such creatures, found in 1999 in Yunnan Province, may be the progenitors of all vertebrates.
At the moment, cartilaginous fish, bone fish (lobe-finned and ray-finned) make up more than half of all living on the planet. In total, there are about 31 thousand species of a wide variety of shapes and sizes that live in salt and fresh water. The study of ancient creatures is a separate science - ichthyology. Let us dwell in more detail on the classes, their features and differences.
cartilaginous fish
The main feature of all representatives of the class is that their skeleton consists of cartilage, which over time, as a result of the deposition of minerals, can become quite hard. Previously, for this reason, they were considered prehistoric animals. However, many of them are characterized by live birth, sometimes even with the formation of a bile placenta - this is how cartilaginous fish differ radically from bone fish.
In addition, they have several more anatomical structural features. First, the absence Therefore, they have to move in order to sink to the bottom of the reservoir. Secondly, cartilaginous fish lack gill covers, and the gills open outwards with characteristic slits. Thirdly, they are all covered which is similar to the teeth of vertebrates. It consists of dentin and a layer of enamel covering it. Such scales are not restored when lost, but with the growth of the fish, its number increases.
Life support systems in cartilaginous fish
The characterization of cartilaginous and bony fish will not be complete if we do not mention the main systems: circulatory, digestive and sexual, in which differences are observed. Cartilaginous have red blood (due to the presence of hemoglobin and red blood cells), which is produced by the spleen. The circulatory system itself in structure resembles that of cyclostomes. Kidneys stretch along the spine in the form of two dark red stripes. The intestines of cartilaginous fish consists of three sections, these are: the large and small intestines, and the rectum. The liver and pancreas are well developed. But the most important thing is that the classes Cartilaginous fish and Bony fish differ in the structure of the reproductive system. The first is characterized by the formation of an egg, which can be laid in the external environment or remain in the lower part of the oviduct. In the second case, the embryo begins to develop in the mother's body.
Classification of cartilaginous fish
All of the currently existing representatives of the class Cartilaginous fish are divided into three superorders.
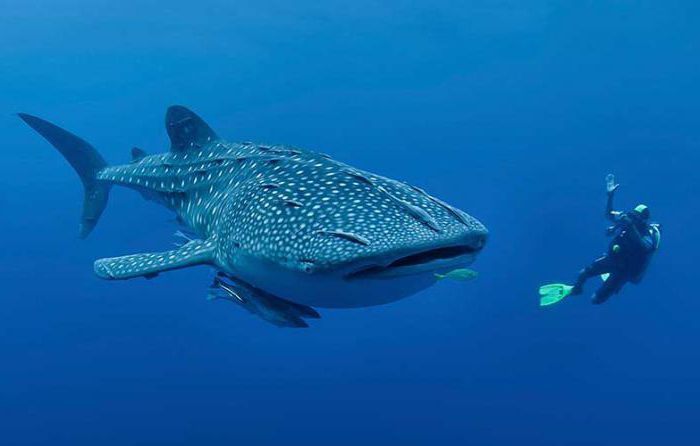

Bony fish: general characteristics
For a long time, until the 21st century, cartilaginous fish, bony fish were considered as two classes. However, in the scientific community, a different point of view is becoming more widespread. So, the Canadian zoologist in his works defines lobe-finned and ray-finned fish in separate classes, and bone ones, respectively, in a superclass. These are the most diverse inhabitants of all types of reservoirs. Their mouth is formed by grasping jaws and teeth located on them, the gills are located on and the nostrils are paired.
Differences from cartilaginous fish
The most important difference between bony fish and cartilaginous fish is clear from the name - the skeleton. He's made of bones. In the internal cavity are located the circulatory, excretion, reproduction and digestion systems. The scales are also characteristic, one of three types: cycloid, ctenoid or ganoid.
The next difference is the presence of a swim bladder located under the spine and filled with gases that secrete blood vessels. With an increase in its volume, the fish easily floats to the surface, with a decrease, it goes into the depths.
Differences have not only external signs of cartilaginous and bony fish, but also reproductive organs, as already mentioned. Most representatives of the second group are characterized by external fertilization occurring in the aquatic environment. This process is called spawning, it occurs at a certain time and is accompanied by characteristic behavior.
ray-finned fish
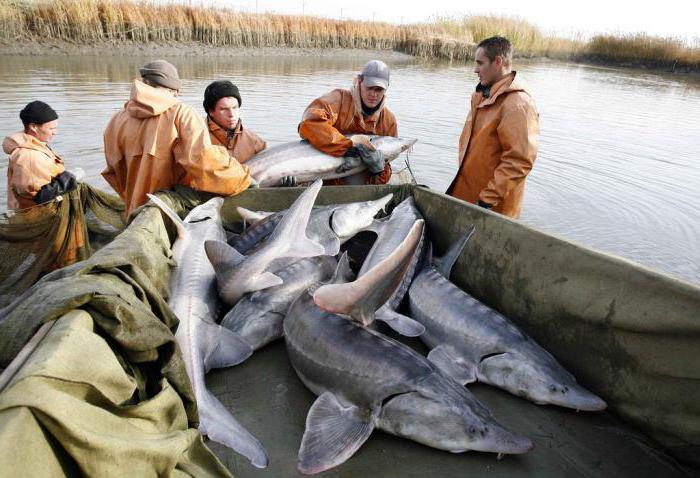
This is the numerically predominant class in the modern diversity of fish, there are more than 20 thousand species, which is about 95%. They inhabit all corners of the planet, from the Arctic seas to the hot equator, the sizes range from 8 mm to 11 meters, and the weight of individual individuals reaches more than two tons. The name, as you might guess, is associated with the structure of paired fins, in which there is no basal axis. The class, in turn, is divided into two groups: New-finned (the most prosperous species) and Bone-cartilaginous fish. The structure of the latter has distinctive features. They have a swim bladder, but at the same time, their skeleton mainly consists of a chord, it has only cartilaginous arches and is not dissected, there are no vertebral bodies as such. A distinctive feature is the rostrum and lower mouth. Many of them are commercial, in particular sturgeon (in the photo below - the catch of the beluga).

lobe-finned fish
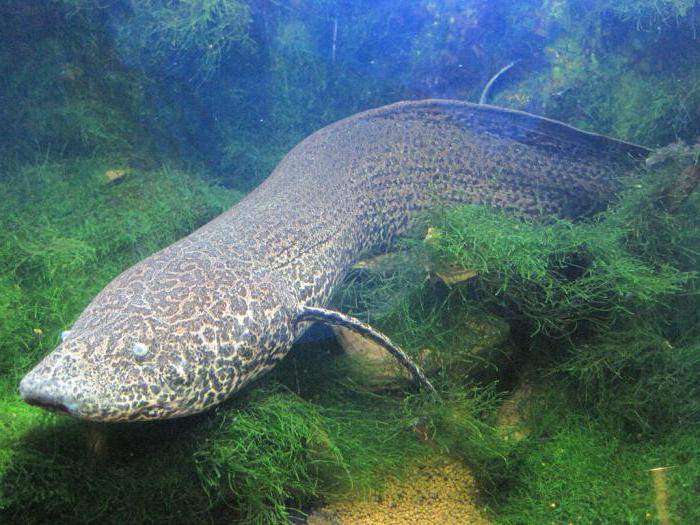
A small class of fish whose skeleton is based on an elastic chord. They combine progressive and archaic features, all representatives belong to two modern superorders - the Crossopterygians and the Lungfishes. Both groups combine ancient fish. Lungfish live in fresh water bodies of Australia, South America and Africa. They have not only gills, but also lungs. This allows them to do without water for some time and feel free in oxygen-depleted water bodies. In total, 6 species are known: four African protopters (photo below), the Australian horned tooth and the South American flake.

Superorder Crossoptera
It is considered nearly extinct. Only one genus has survived to this day - Latimeria (pictured below), numbering two species. Moreover, both of them were discovered relatively recently, the first copy was caught in the Indian Ocean in 1938. It is believed that lobe-finned fish are inhabitants of fresh water bodies in which there was a lack of oxygen. In this regard, they developed musculature at the base of the fins and a dual mode of breathing (lungs and gills). This allowed some subsequently to move back to the seas, and freshwater eventually died out. There is an assumption that it was the lobe-finned fish that gave rise to the class Amphibians.

Thus, cartilaginous fish, bone fish have a number of individual characteristics. The main ones are observed in the structure of the skeleton (cartilaginous or bone), the presence or absence of a swim bladder, the type of scales, the reproductive system and the method of reproduction.