Education
What is the salinity of water? Salinity of the waters of the oceans
March 29, 2017Our planet is covered by water by 70%, of which more than 96% is occupied by oceans. This means that most of the water on Earth is salty. What is the salinity of water? How is it determined and what does it depend on? Can this water be used on the farm? Let's try to answer these questions.
What is the salinity of water?
Most of the water on the planet has salinity. It is commonly referred to as seawater and is found in the oceans, seas, and some lakes. The rest is fresh, its amount on Earth is less than 4%. Before you understand what the salinity of water is, you need to understand what salt is.
Salts are complex substances that consist of cations (positively charged ions) of metals and anions (negatively charged ions) of acidic bases. Lomonosov defined them as "fragile bodies that can dissolve in water." Many substances are dissolved in sea water. It contains sulfates, nitrates, phosphates, sodium, magnesium, rubidium, potassium cations, etc. Together, these substances are defined as salts.
So what is the salinity of water? This is the content of dissolved substances in it. It is measured in thousandths - ppm, which are indicated by a special symbol -% o. Ppm is the number of grams in one kilogram of water.
What determines the salinity of water?
In different parts of the hydrosphere and even at different times of the year, the salinity of the water is not the same. It changes under the influence of several factors:
- evaporation;
- ice formation;
- precipitation;
- melting ice;
- river flow;
- currents.
When water evaporates from the surface of the oceans, the salts remain and do not erode. As a result, their concentration increases. Freezing has a similar effect. Glaciers contain the largest supply of fresh water on the planet. During their formation, the salinity of the waters of the World Ocean increases.
The melting of glaciers is characterized by the opposite effect, reducing the salt content. In addition to them, the source of fresh water is precipitation and rivers flowing into the ocean. The salt level also depends on the depth and nature of the currents.
Their highest concentration is on the surface. The closer to the bottom, the less salinity. Warm currents affect the salt content in a positive direction, cold ones, on the contrary, reduce it.
Related videos
Salinity of the oceans
What is the salinity of sea water? We already know that it is far from the same in different parts of the planet. Its indicators depend on geographic latitudes, climatic features of the area, proximity to river objects, etc.
The average salinity of the waters of the World Ocean is 35 ppm. Cold regions near the Arctic and Antarctic are characterized by a lower concentration of substances. Although in winter, when ice forms, the amount of salt increases.

For the same reason, the least saline ocean is the Arctic Ocean (32% o). The Indian Ocean is the highest. It covers the area of the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, as well as the southern tropical zone, where the salinity is up to 36 ppm.
The Pacific and Atlantic oceans have approximately equal concentrations of substances. Their salinity decreases in the equatorial zone and increases in subtropical and tropical regions. Some warm and cold currents balance each other. For example, the non-salty Gulf Stream and the salty Labrador in the Atlantic Ocean.
Salinity of lakes and seas
Most of the lakes on the planet are fresh, as they are fed mainly by precipitation. This does not mean that there are no salts in them at all, just that their content is extremely small. If the amount of dissolved substances exceeds one ppm, then the lake is considered salty or mineral. The Caspian Sea has a record value (13% o). The largest fresh lake is Baikal.
Salt concentration depends on how the water leaves the lake. Fresh water bodies are flowing, while more saline ones are closed and subject to evaporation. The determining factor is also the rocks on which the lakes formed. So, in the area of the Canadian Shield, rocks are poorly soluble in water, and therefore the reservoirs there are “clean”.

The seas are connected to the oceans through straits. Their salinity is somewhat different and affects the average ocean waters. Thus, the concentration of substances in the Mediterranean Sea is 39% o and is reflected in the Atlantic. The Red Sea, with an indicator of 41%, greatly raises the average salinity of the Indian Ocean. The most salty is the Dead Sea, in which the concentration of substances ranges from 300 to 350% o.
Properties and significance of sea water
Salt water is not suitable for economic activity. It is not suitable for drinking, as well as watering plants. However, many organisms have long adapted to life in it. Moreover, they are very sensitive to changes in its salinity. Based on this, organisms are divided into freshwater and marine.
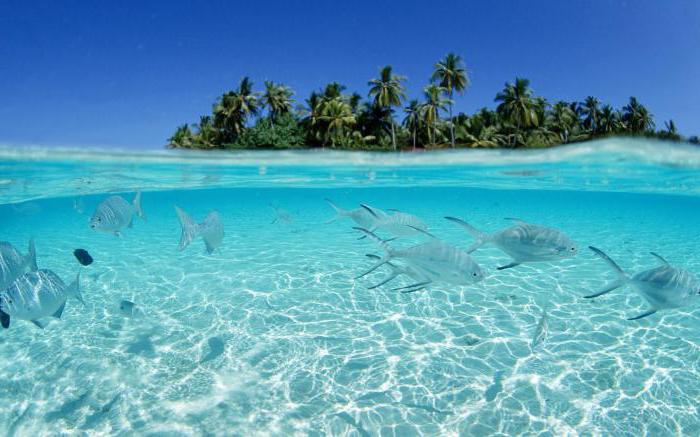

So, many animals and plants that live in the oceans cannot live in the fresh water of rivers and lakes. Edible mussels, crabs, jellyfish, dolphins, whales, sharks and other animals are exclusively marine.
People use fresh water for drinking. Salt is used for medicinal purposes. In small quantities, water with sea salt is used to restore the body. The therapeutic effect is produced by bathing and taking baths in sea water.