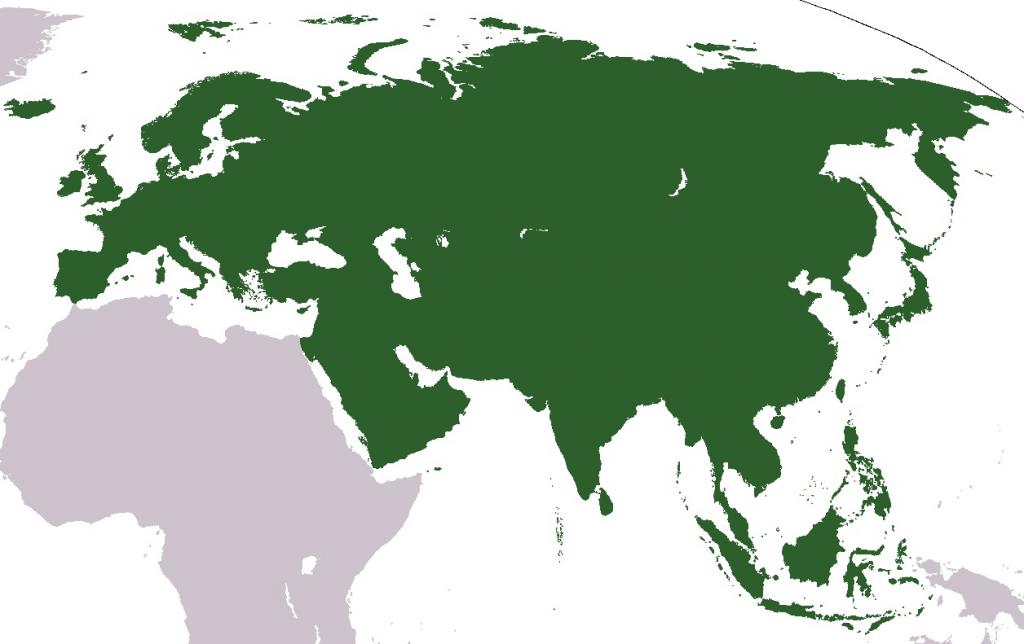
Eurasia is the largest continent by area. It accounts for 36% of the entire land mass of the globe. Three-quarters of the world's population lives on its territory and 94 official states are located. What are the features of the mainland? You will find a description of the geographical location of Eurasia, its climate, nature and other characteristics in our article.
Due to its great extent and unique geographical position, Eurasia has a huge natural diversity and is a record holder in many respects. Here are just some of its features:
- Most of the ancient civilizations developed in Eurasia, the greatest discoveries were made here and the main world religions arose. It was from here that the first research ships sailed.
- Here is the largest country in the world - Russia, whose area is 17,100,000 km².
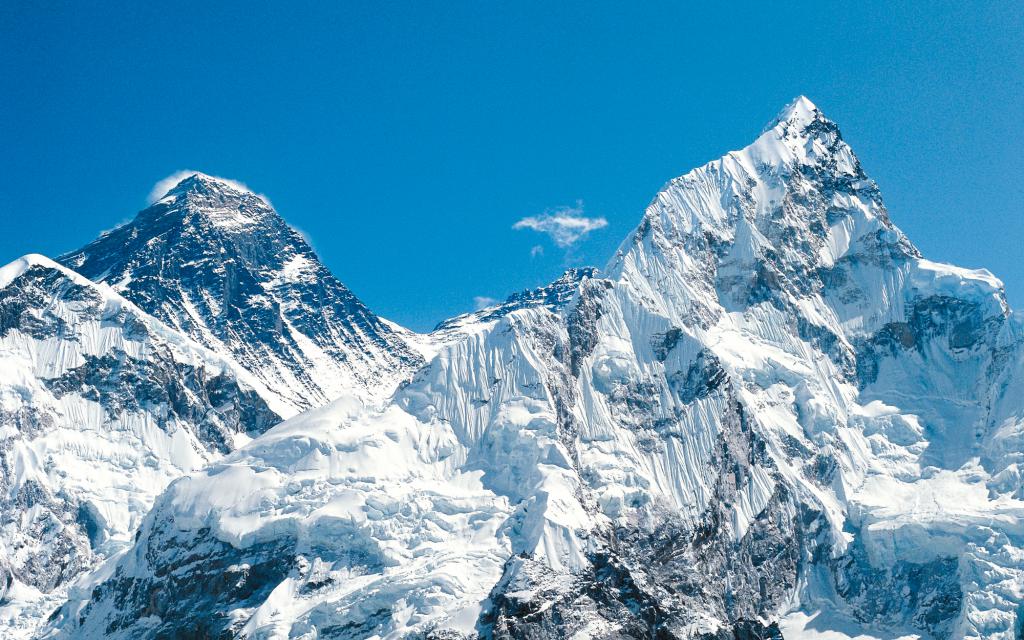
- There are many mountains on the mainland. In its Asian part, there is the highest mountain system (Himalayas) and the largest system by area (Tibet). Its highest point is Chomolungma, or Everest, reaching 8848 meters.
- The Arabian Peninsula in the south of the continent is the largest in the world and covers an area of 3.25 million km².
- The mainland has the largest lake (Caspian Sea), the deepest freshwater lake (Baikal) and the narrowest strait (Bosphorus).
Description of the geographical position of the Eurasian continent
Eurasia occupies 54.3 million km2. The main part of the mainland is located in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres of the planet. It includes two parts of the world - Europe and Asia, which are separated by a conditional border drawn along the main natural objects (the Ural Mountains, the Caspian Sea, etc.).
The main feature of the geographical position of Eurasia is that it is washed by all the oceans: the Indian in the south, the Arctic in the north, the Atlantic in the west and the Pacific in the east. It is closest to Africa, separating from it. the Mediterranean and Red Seas, the Suez Canal and the Strait of Gibraltar. In addition to continental land, it also includes a huge number of islands, the total area of \u200b\u200bwhich exceeds 3 million km 2.
From west to east, Eurasia stretches for 18 thousand km, and from north to south - for 8 thousand km. Its extreme mainland and island points:
- western - Cape Roca in Portugal and rock Monchik in the Azores;
- eastern - Cape Dezhnev and Ratmanov Island in Russia;
- northern - Cape Chelyuskin and Cape Fligeli in Russia;
- southern - Cape Piai in Malaysia and the South Island in Keeling (Cocos Islands).
Relief
The relief of the mainland is uneven and is represented by both lowlands and significant elevations of the landscape. In its northern part is the East European Plain - one of the largest in the world. It stretches within 12 states from the shores of the Baltic and Black Seas to the Caspian Sea and the Ural Mountains.
In the relief of the mainland, the West Siberian Plain, the Tibetan Plateau, the Turan lowland, the Indo-Gangetic, and the Great Chinese Plains are also distinguished. On its territory there are high and medium mountain systems, such as: the Alps, the Caucasus, the Carpathians, the Himalayas, the Urals, the Tien Shan and others. The average elevation of Eurasia is approximately 830 meters.

Climate
The geographical position of Eurasia largely determines its climate. It is represented on the mainland by all belts and natural areas. In the north, part of its territory is located beyond the Arctic Circle. Here is a zone of subarctic and arctic deserts, where most of the year there are snow and low temperatures.
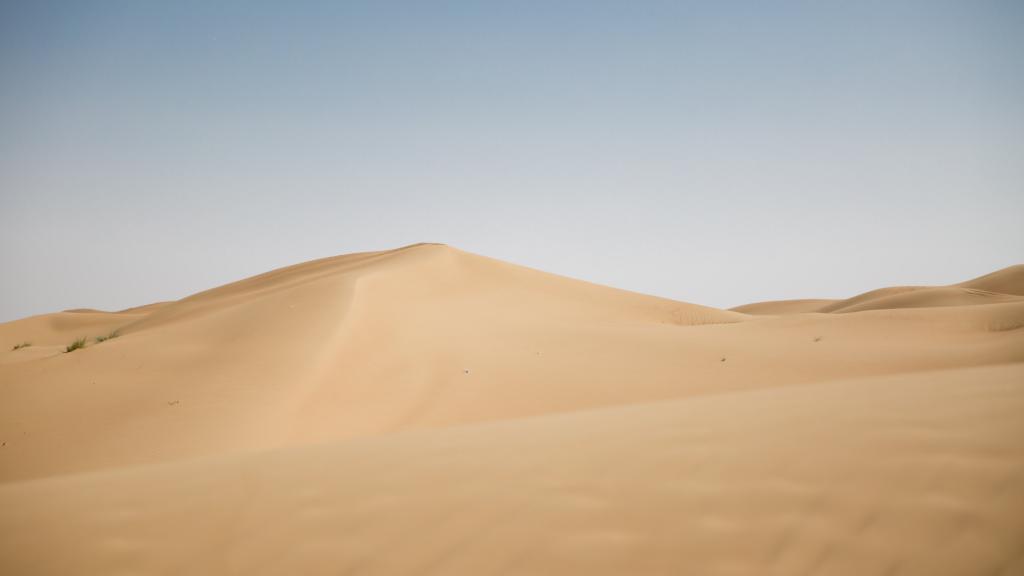
The central regions of Eurasia are covered by a temperate zone, which stretches along its entire length: from the western to the eastern coast. In the Asian part of the mainland, in the region of the Arabian Peninsula and partly of Hindustan, there is a tropical zone represented by hot and arid deserts.

To the east are the subequatorial and equatorial belts. They are characterized by heavy seasonal or year-round precipitation, frequent typhoons and hurricanes. In the European part, the tropical, subequatorial and equatorial belts are not represented. In the south, there are subtropics with maritime and arid climate types.
Due to the geographical position of the Eurasian continent, the action of ocean currents is strongly displayed on it. Thus, the waters of the Atlantic greatly soften the conditions in the European part, making winters milder and summers cooler. In the depths of the mainland, where sea winds do not reach, the climate is arid continental. In the east (especially on the coast), the climate changes twice a year, sometimes under the influence of wet monsoons, sometimes under the influence of dry winds from the continent.
Nature of the continent
The geographical position of Eurasia is similar to the position of North America. Both continents are located between the arctic and equatorial climatic zones. But due to the vast area of Eurasia, some natural zones are much more pronounced on it, and latitudinal zonality can be traced more clearly.
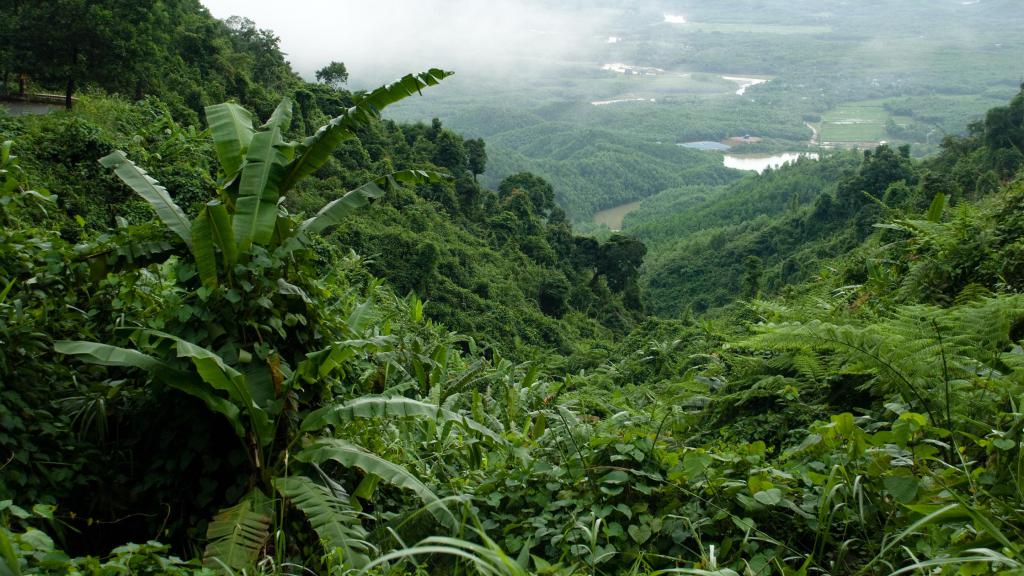
A large number of natural complexes and all existing natural zones are represented on the mainland. In the north there are areas of permafrost, permanent ice and snow. Polar bears, polar hares, owls and polar foxes live here. Slightly lower stretch areas of the tundra with marshy wastelands, lichens and mosses, and even lower begins the taiga with dense coniferous and mixed forests.
The southern and central regions of the mainland are no less diverse. Depending on the specific area, they are found in forests and forest-steppes, wet grassy meadows, dry steppes, lifeless deserts, evergreen jungles and mangroves.

There are many full-flowing rivers, swamps and lakes in the northern and coastal regions of the continent. Some of the powerful streams begin in the mountains. At the same time, the territory of the Arabian Peninsula and the Thar Desert is considered the driest in Eurasia. There are no permanent rivers here, and the only salvation is underground springs and occasional seasonal rains. Deserts are also present in Central Asia.
Uniqueness of Eurasia
Each continent of our planet has its own unique features and peculiar geographical position. Eurasia can be called special due to the fact that it is surrounded by all four oceans and is located in all climatic zones. This is the largest and longest continent on the planet from west to east - in size it is almost twice the size of Africa, and Australia - seven times. The combination of all the factors that shape Eurasia has contributed to its great diversity and made it unique.