At certain intervals of time, called the seasons of the year. Each such period is characterized by its meteorological anomalies.
Natural phenomena in spring
For 3 months of this time of the year, the climate and living conditions of all fauna and flora change beyond recognition.
With the onset of March, nature is just beginning to come to life and wake up from the winter period of "hibernation". By this time, the heat of the sun's rays is still insufficient for the complete melting of snow, but the air is already noticeably warming up. In March, the first spring natural phenomena make themselves felt (examples: ice drift, thawed patches, south wind). At this time, the clouds rise noticeably and acquire a cumulus character.
From the first days of April, the time comes for the most "gray" meteorological anomalies. The names of natural phenomena of this time are known to everyone: fogs, drizzling rains, less often thunderstorms. By the middle of the month, the snow has completely disappeared, but the rivers can still be dangerous with heavy ice drift. Fortunately, the air temperature is warming up every day, so the consequences of winter frosts will soon cease to make themselves felt. Also in April, dangerous spring floods, heavy winds caused by the connection of the south stream with the north one are not ruled out.
As for the fauna, it begins to fully come to life by the first days of May.
Spring Phenomena: Rain
With warming comes precipitation in liquid form. Such natural phenomena (see pictures below) are called rains or showers. It is a continuous stream of water directed vertically from the sky to the earth. Clouds gradually accumulate moisture, and when pressure and gravity begin to prevail over them, precipitation falls. Since the air temperature is above 0 degrees, it means that water molecules do not crystallize into snowflakes. On the other hand, in rare cases, hail is possible closer to May.

Rain is one of the 5 natural phenomena of spring that are likely to pose a threat to the economy and agriculture. Prolonged precipitation can flood not only streets and private houses, but also fields with seedlings and sprouts, which will subsequently rot, therefore, yields will drop significantly.
At the moment, it is customary to distinguish the following types of rain:
- ordinary (precipitation without such pronounced features as thickness, duration);
- torrential rain (short-term rain, characterized by suddenness and force of precipitation);
- protracted (characterized by a long duration, up to several days, and a decrease in air temperature);
- short-term (characterized by the transience and abrupt end of precipitation);
- snowy (characterized by a decrease in air temperature and partial crystallization of water molecules);
- mushroom (during such rain, the sun's rays continue to reach the earth);
- hail-shaped (short-term and dangerous downpour, falling partially in the form of ice floes).
Spring Phenomena: Thunderstorm
This meteorological anomaly is a separate type of rain that is not included in the traditional classification. A thunderstorm is a precipitation that occurs simultaneously with thunder and lightning.
For several days, clouds accumulate moisture particles picked up by strong winds. Gradually, dark cumulus clouds form from them. During precipitation with high power and heavy wind, an electrical tension arises between the earth's surface and clouds, during which lightning is formed. This effect is always accompanied by a strong thunder. Such natural phenomena (you can see the pictures below) most often occur at the end of spring.

For a thunderstorm to occur, the following conditions are necessary: uneven heating of the lowest layers of air, atmospheric convection, or a sharp intensity of cloud formation in mountainous areas.
Spring phenomena: wind
This climatic phenomenon is a stream of air that is directed along the horizontal axis. Such spring natural phenomena as wind and storm (in rare cases) are characterized by high speed, force of impact, area of distribution and noise level.
From the point of view of meteorology, this climatic anomaly consists of indicators of direction, power and duration. The strongest air currents with medium gusts are called squalls. With regard to duration, the winds are as follows: hurricane, storm, breeze, typhoon, etc.
In some parts of the Earth, monsoons occur due to frequent temperature changes. Such global winds are characterized by a long duration (up to 3 months). If such air flows are caused by a difference in temperature relative to latitudes, then they are called trade winds. Their duration can be up to a year. The border between the monsoons and the trade winds is called Spring and autumn, it is especially noticeable in countries with a temperate climate. In the tropical regions of the planet, it is due to the wind that the weather and air temperature change so often.
Spring phenomena: clouds
Closer to mid-March, the sky gradually begins to thin out. Now the clouds have clear boundaries. By themselves, they are a product of the condensation of water vapor particles in the upper atmosphere.

Clouds form over the earth's surface. The main condition for their formation is warm moist air. It begins to rise to the top where, with a noticeable decrease in temperature, it stops at a certain height. Essentially, clouds are made up of water vapor and ice crystals. Their large accumulation at high concentration forms cumulus clouds.
All spring natural phenomena have their own forms of uniqueness, which are called meteorological identifiers in science. At high temperatures, the clouds are filled with drop elements, and at low temperatures, with crystalline ones. Regarding this criterion, there is a separate classification of the phenomenon. So, clouds are divided into rain, thunderstorm, cirrus, stratus, cumulus, mother-of-pearl, etc.
Spring events: melting snow
With an increase in the temperature of the air, frozen water crystals begin to gradually turn into water. This process is called snowmelt. All frozen ones are subject to such dissolution if the air temperature rises to 0 degrees. These seasonal phenomena in nature occur only in spring. The exact time up to a month is set depending on the current climate.
The process of snow melting is markedly accelerated by rainfall. After that, small temporary reservoirs are formed. Snow melts fastest on flat terrain, where there are no barriers to the wind or a canopy from precipitation. In the forest, this process can take up to a month. In this case, the probability of raising the level of groundwater is high.

Often the snow begins to evaporate in frosty weather. This natural phenomenon is called sublimation. Under the influence of sunlight, water particles pass from a solid state to a gaseous state.
Spring phenomena: ice drift
This anomaly is considered the most dangerous of natural phenomena at this time of the year. This phenomenon is the movement of half-melted ice floes on lakes and rivers under the influence of a strong wind or current. The greatest movement is observed in the middle of the reservoir. Such spring natural phenomena are typical for March, when they are able to sufficiently warm the temperature of the air and soil.
On the rivers, ice drift is often accompanied by traffic jams. In large reservoirs, this phenomenon is determined by the drift of fragments under the action of the wind. The intensity of ice movement, as well as its nature, directly depends on the current climatic conditions, the time of opening, the structure of the riverbed and the hydraulic properties of the water flow.
The duration of this process in the spring varies within 3-4 weeks. Landscape and climate play an important role here.
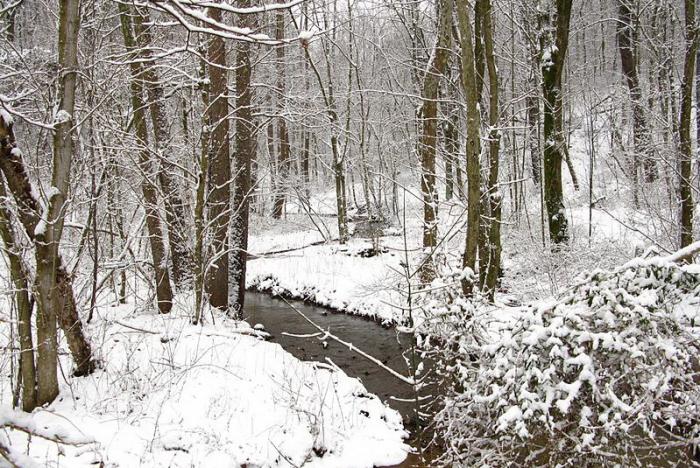
Spring phenomena: thaw
Usually this process begins in early March, but depending on climatic conditions, the dates may move to mid-April. A thawed patch is a place where there was snow in frosty weather, and with warming, a kind of funnel appeared on it. Such spring natural phenomena are very interesting to study.

First of all, thawed patches form around tree trunks, as heat comes from the root system of plants, supported by solar synthesis. Further, the process affects fields and swamps. The thawed spots can be of different colors, depending on how the surface looks (earth, grass, leaves). The situation is similar with their form. In the fields, the thawed patches are elongated, like beds, in the gardens they are rounded (projection of tree trunks).
This process begins to take effect at an average daily temperature of -5 degrees and above.
Spring phenomena: the awakening of the flora
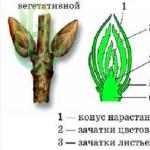
The appearance of thawed patches around the trees indicates that the plants have begun active sap flow. These seasonal phenomena in nature mean only one thing - the awakening of the flora after a long winter passive life.
You can check this very easily. To do this, it is enough to pierce the bark of a tree with a needle or a thin knife. If a transparent sweet liquid of a pale reddish color appears at this place, then the sap flow is in full swing. This indicates that nature is preparing for gardening.
Soon buds will appear on the branches and bloom. In the second half of spring, thanks to the wind and insects, the flora will receive pollination. Therefore, a harvest can be expected in the near future.
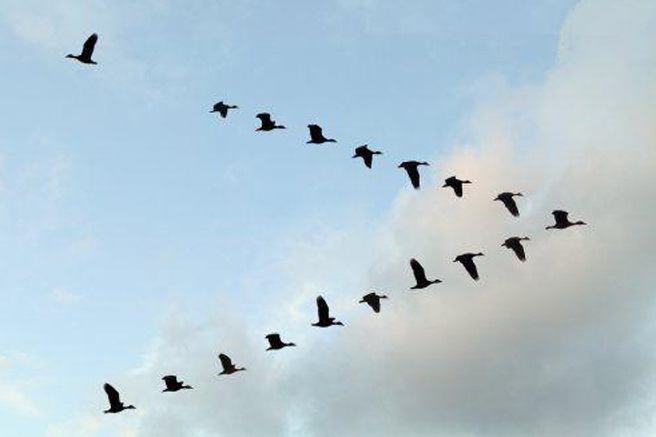
Spring phenomena in wildlife
As you know, this time of year is marked by the return of birds from warm countries. First of all, this applies to rooks. They are considered the first heralds of spring. Mass migration of birds occurs towards the end of March, when the night air temperature rises to +10 degrees.

Also, one of the indicative processes in wildlife that characterize the onset of spring are the molting of animals and the awakening from hibernation of wild animals. The change of coat occurs in March, although in some representatives of the fauna it may also be in autumn.
It is very important to know all these spring natural phenomena. It is not for nothing that natural science is included in the main curriculum of school subjects. Knowing the fundamental processes of climate and nature is the duty of every person on the planet.